Tesla electric vehicles are a game-changer in the automotive industry. With sleek designs, cutting-edge technology, and impressive performance, it’s no wonder why so many people are choosing to switch to Tesla. However, it’s important to note that one of the key features of a Tesla vehicle is the battery—specifically, how long it lasts.
A fully-charged Tesla battery covers a distance of between 250 and 400+ miles, depending on the car model. Overall, a Tesla battery is good for roughly 1,500 cycles or between 300,000 and 500,000 miles.
In this guide, we’ll go over the basics of electric vehicles and what Tesla batteries are made of. I’ll also include a few pointers on how you can extend the lifespan of your Tesla.
What Is a Tesla?
An electric vehicle (EV) is a vehicle that is propelled by an electric motor rather than a traditional gasoline engine. The electricity is stored in a battery pack and charged by connecting to the power grid. Electric vehicles emit no tailpipe emissions, making them a more environmentally friendly and sustainable option than traditional gas-powered vehicles.
Tesla electric vehicles distinguish themselves from other EVs in several ways. For starters, Tesla vehicles have a long range, allowing drivers to travel over 300 miles on a single charge, depending on the model. Tesla also has a large Supercharger network, which allows for quick and easy charging on long trips. Furthermore, Tesla vehicles feature cutting-edge technology, such as advanced driver assistance systems, a large touchscreen display, and over-the-air software updates that continuously improve the vehicle’s performance and features.
Tesla is also a sustainability leader, having pledged to use renewable energy to power their manufacturing processes and charging infrastructure. The Musk-led automotive company is leading the charge in the transition to a cleaner and more efficient future by focusing on sustainable transportation.
What Are Tesla Batteries Made of?
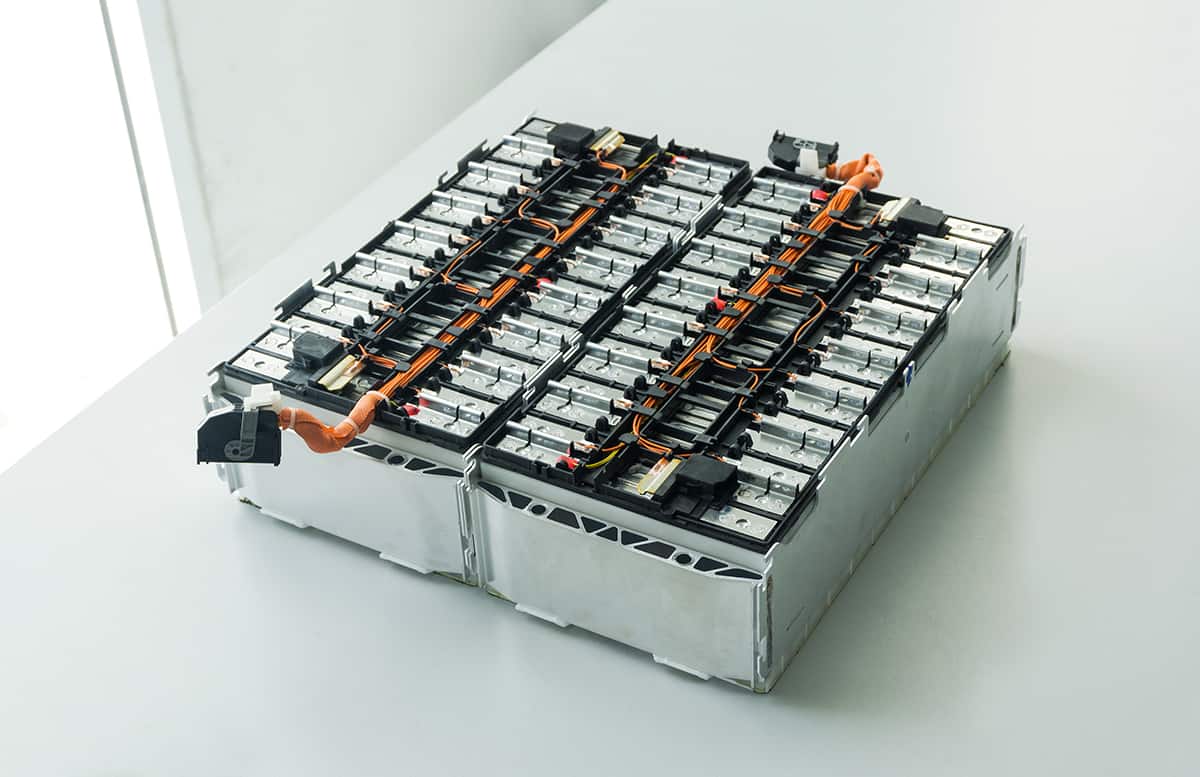

Tesla batteries are primarily made of lithium-ion cells, with cathodes composed of different materials depending on the model of the vehicle. In some of its vehicles, Tesla uses nickel-cobalt-aluminum (NCA) cathodes developed by Panasonic, which have a higher energy density but also contain cobalt, a material associated with human rights abuses in its mining process. However, for its standard-range vehicles, Tesla uses lithium-iron-phosphate (LFP) cathodes, which are cobalt- and nickel-free.
In terms of lithium content, Elon Musk has described lithium as “the salt in your salad,” as it makes up about 2% of the cell mass in a Tesla battery. While lithium might not be the most abundant raw material in the battery, it can still be a crucial component, and its supply chain has become increasingly important with the growth of the electric vehicle market. Tesla has also explored new methods to extract lithium from clay, which could potentially reduce the cost and environmental impact of lithium production.
How Long Does A Tesla Battery Last?
The range of a Tesla is largely determined by the vehicle’s model. The Model 3 has a smaller internal battery with a range of about 358 miles, whereas the more expensive Model S has a larger and more efficient battery with a range of more than 400 miles. The actual range experienced by an EV owner may be influenced by a number of factors, including vehicle speed, driving conditions, and battery age.
One of the main concerns for EV owners is battery life, and Tesla has been at the forefront of addressing this issue. Tesla is well-known for its long-lasting batteries, which can travel between 300,000 and 500,000 miles.
According to a Tesla report, even after 200,000 miles, the Model S and X batteries retain more than 80% of their capacity. Tesla also guarantees at least 70% battery retention for 8 years or 100,000 to 120,000 miles. One study found that Tesla vehicles lose only 5% of their capacity in the first 50,000 miles and can travel more than 150,000 miles before losing 10% of their initial battery life.
Tesla Drive Range per Charge
| Model | Estimated Range |
| Model 3 Long Range | 358 miles |
| Model 3 Performance | 315 miles |
| Model S | 405 miles |
| Model S Plaid | 333 miles |
| Model X | 348 miles |
| Model X Plaid | 33 miles |
| Model Y Long Range | 330 miles |
| Model Y Performance | 303 miles |
Can You Replace Tesla Battery?
Yes, you can replace the battery in a Tesla vehicle. The cost of a battery replacement varies depending on the model of the vehicle and whether you opt for a new or remanufactured battery. According to Elon Musk, a complete battery replacement for a Tesla vehicle costs between $20,000 and $35,000, but actual prices can vary.
An invoice from Tesla showed that a complete battery replacement for a Model 3 costs $16,550.67. However, third-party repair shops may offer the service at a lower cost, but it is important to be cautious when choosing a shop as Tesla doesn’t authorize these.
Why Are EV Batteries So Expensive?
Several factors contribute to the high cost of EV batteries. For starters, the cost of manufacturing is inflated because of the rarity and high price of battery components like lithium and cobalt. A second factor adding to the high price is the complexity and unique machinery needed to manufacture EV batteries.
Demand for EVs is still low compared to traditional gas-powered vehicles, which contributes to the lack of economies of scale in battery production. This results in a higher cost of production per battery, which drives up the price of the batteries.
Battery packs for EVs are also expensive because they are made to last for a long time and hold a lot of energy. A key part of an EV is the battery pack, and it’s important to ensure its reliability and longevity, but doing so can be costly.
Last but not least, there is the added expense of continuing to invest in research and development to advance battery technology and boost its efficiency. Companies like Tesla are pouring resources into R&D to develop cheaper, better batteries, but this will take some time.
Tips for Extending EV Battery Life
Assuming your Tesla performs as intended and reaches the 500,000-mile mark before being converted into scrap metal, that’s still roughly 2 times the amount of travel range than the typical gas-powered vehicle. However, if you’d like to squeeze out a few extra thousand miles per battery, here are a few things you can try.
1. Keep your EV away from extreme temperatures when not in use
The most common risk occurs when people leave their cars parked in the sun without plugging them in. Your electric car’s battery life will be drastically reduced if you install an automatic temperature control system. Maintain a consistent temperature range during operation by parking your electric vehicle in the shade or plugging it into an outlet when not in use, as the thermal management system will only operate when using grid power.
2. Do not charge your EV to 100% every day

Batteries in electric vehicles are protected from being charged or discharged to their maximum or minimum capacity by a system called battery management. Maintaining a charge level from 0 to 100% is also beneficial to the performance and longevity of your vehicle’s battery. While a full charge will provide the longest possible use time, doing so is bad for the battery in the long run.
3. Don’t use fast charging
Fast charging is incredibly helpful if your batteries are about to die. However, it draws a lot of current from the batteries quickly, which puts stress on them and shortens their lifespan. Eight years of standard charging will give you 10% more battery life compared to eight years of using fast charging, despite the fact that its degradation is barely perceptible.
4. Avoid abrupt acceleration
Doing this in an EV puts stress on the battery and motor, reducing the overall lifespan of the battery and potentially decreasing its range and performance. Additionally, abrupt acceleration can also lower the efficiency of the vehicle and increase the energy consumption, draining the battery faster. To maintain the battery life, it is recommended to drive smoothly and efficiently, avoiding sudden acceleration and braking.
5. When not using your EV, charge it only to the above “low” status
The battery life of electric vehicles degrades whether the vehicle is parked or stored with a full or empty battery. If you don’t plan on using your electric car very often or if you have a long trip planned, invest in a timed charger and leave it plugged in. If you leave your car with a full battery and leave it parked in one spot for a long time, the battery will have a hard time staying charged.
It is possible to keep the battery charged at an average level somewhere between 25% and 75% of its capacity by adjusting the charger’s settings so that it never fully charges the battery.
6. Read the owner’s manual to see how to properly charge the EV
The charging process, including the recommended charging times, the type of charger to use, and the proper way to connect the charger to the vehicle, is covered in detail in the manual. Instructions on how to maintain the battery and keep it in good shape are included as well.
Any problems that may arise during the charging process can be remedied by consulting the owner’s manual. Instructions for resetting the vehicle’s battery management system and dealing with other charging-related problems may be included.






