Wear and tear is the primary reason piston rings go bad, but factors like poor maintenance, high operating temperatures, and using low-quality parts can also contribute. To fix them, you typically need to replace the damaged rings, which involves disassembling the engine to access the piston and rings.
Whether you own a classic Charger or a modern Ram, swapping your engine can give your ride a new lease on life, increase horsepower, and even improve fuel economy. This guide will help you understand Dodge engine swap compatibility. It covers everything from the basics of engine swaps, specific Dodge models and engine options, to a comprehensive compatibility chart to help you make an informed decision.
If you own a Jeep Wrangler or are thinking about buying one, you’ve probably wondered about the interchangeability of parts between different years and models. Knowing which parts can be swapped can save you money, offer more customization options, and even help you source hard-to-find components.
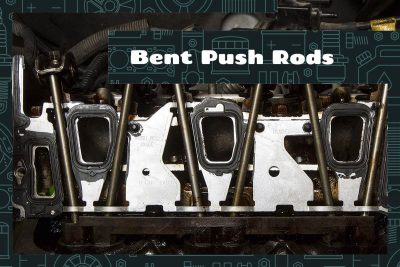
Signs of bent push rods include reduced engine power, strange knocking or tapping noises, and warning lights on the dashboard. If your car has bent push rods, your only option is to replace them.
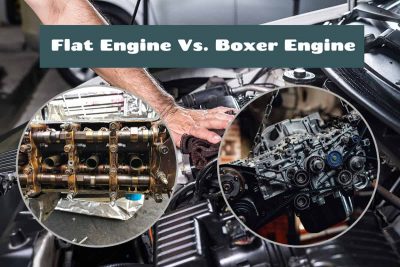
The design of an engine determines how that vehicle performs. Among the various engine configurations available, flat and boxer engines have gained a distinct reputation for their unique design and the performance attributes they offer. Both these types boast a different take on engine layout.
The “Service Engine Soon” light serves as a maintenance reminder, though it may also indicate potential engine or emission problems. This light can be triggered by various issues, ranging from minor concerns like a loose gas cap to major ones like engine malfunctions.
Every car owner knows the unmistakable sound of a vehicle starting up—the revving of the engine after the turn of a key or push of a button. This action is due to the starter, which initiates the engine’s operation. But what if the starter doesn’t behave as expected?
The fuel pump relay controls the operation of the fuel pump, ensuring the engine gets the correct amount of fuel. Its efficiency is crucial for optimal vehicle performance, and a faulty fuel pump relay can cause a slew of problems, ranging from starting issues to total vehicle breakdown.
Bad starter relay symptoms typically include problems starting the car, unusual noises during ignition, and irregular engine cranking. You’ll usually find the starter relay in the fuse box under your car’s hood or dash. The replacement cost, including parts and labor, often ranges from $50 to $250, depending on the model of your vehicle.
Driving through water might seem like a harmless act, especially during rainy seasons or when encountering flooded areas. However, doing so can lead to several complications for your vehicle, such as starting problems. The worst of which is your car being unable to start at all!
Most of the time, people are scratching their heads over how to get their cars started. However, there may be specific instances where you want the opposite—to prevent your car from turning on completely. So, how do you do this?
If your car is at a full stop, turning it off while in drive won’t do anything except shut off the engine. If your car is in motion, doing this will result in losing power steering and braking, making the car more difficult to control.