The transmission system of your vehicle is an integral part that ensures the smooth functioning of your car. But what happens when you notice that the transmission is hot even when the engine is at idle? This issue can be alarming and may indicate a problem with your car that needs immediate attention.
There are several possible causes for a hot idle transmission, including:
- Lack of transmission fluid
- Malfunctioning transmission cooler
- Clogged transmission filter
- Electrical issues
Fortunately, with proper diagnosis and timely fixes, you can resolve this issue and restore your vehicle’s transmission to its optimal performance. In this blog post, we will explore the causes and fixes of a hot idle transmission to help you keep your car running smoothly.
What Causes Transmission Hot Idle Engine?
When your transmission system overheats while the engine is idle, it can be a sign of underlying problems that require prompt attention. Understanding the root cause of the issue is crucial in identifying the appropriate solutions to fix it. In this section, we will delve into the common causes of transmission hot idle engines and how they affect your vehicle’s performance.
1. Lack of transmission fluid
Low transmission fluid levels are a common cause of hot idle transmission. The fluid has important roles, including lubricating the moving parts, transferring power, and regulating temperature. When the fluid levels are low, it increases friction and heat buildup, which can lead to overheating of the transmission.
Neglecting low transmission fluid levels can cause significant damage to the transmission system of your vehicle, resulting in costly repairs or replacements. Moreover, running your vehicle with low fluid levels can reduce fuel efficiency and affect its performance.
2. Malfunctioning transmission cooler
The transmission cooler is responsible for keeping the transmission fluid at a safe temperature. It does this by sending the fluid through a radiator. If the cooler is not working as it should, it can cause the transmission to overheat.
A bad transmission cooler can lead to several problems, like the transmission slipping, hard shifting, and, eventually, complete failure of the transmission system. Additionally, driving with a faulty transmission cooler can also hurt fuel efficiency and performance.
3. Clogged transmission filter
The transmission filter is important for keeping the transmission fluid clean by removing dirt and other particles. But if the transmission filter gets clogged with debris over time, the fluid flow can be restricted, and the transmission may overheat. This can cause problems like reduced fuel efficiency, poor performance, and even transmission failure.
4. Electrical issues
Today’s vehicles use complex electrical systems to regulate and control many components, including the transmission system. Faults in the electrical system, such as damaged wires, corroded connectors, or faulty sensors, can cause the transmission to overheat.
This can lead to issues like transmission slipping, hard shifting, or reduced acceleration. Running a vehicle with electrical problems can also negatively affect its fuel efficiency and overall performance.
What Are the Signs of Transmission Hot Idle Engine?
The signs of a transmission hot idle engine can be easy to miss, but they are important to pay attention to in order to catch the issue early and prevent more serious damage to your vehicle. Here are some common signs that your transmission may be overheating:
1. Temperature warning light
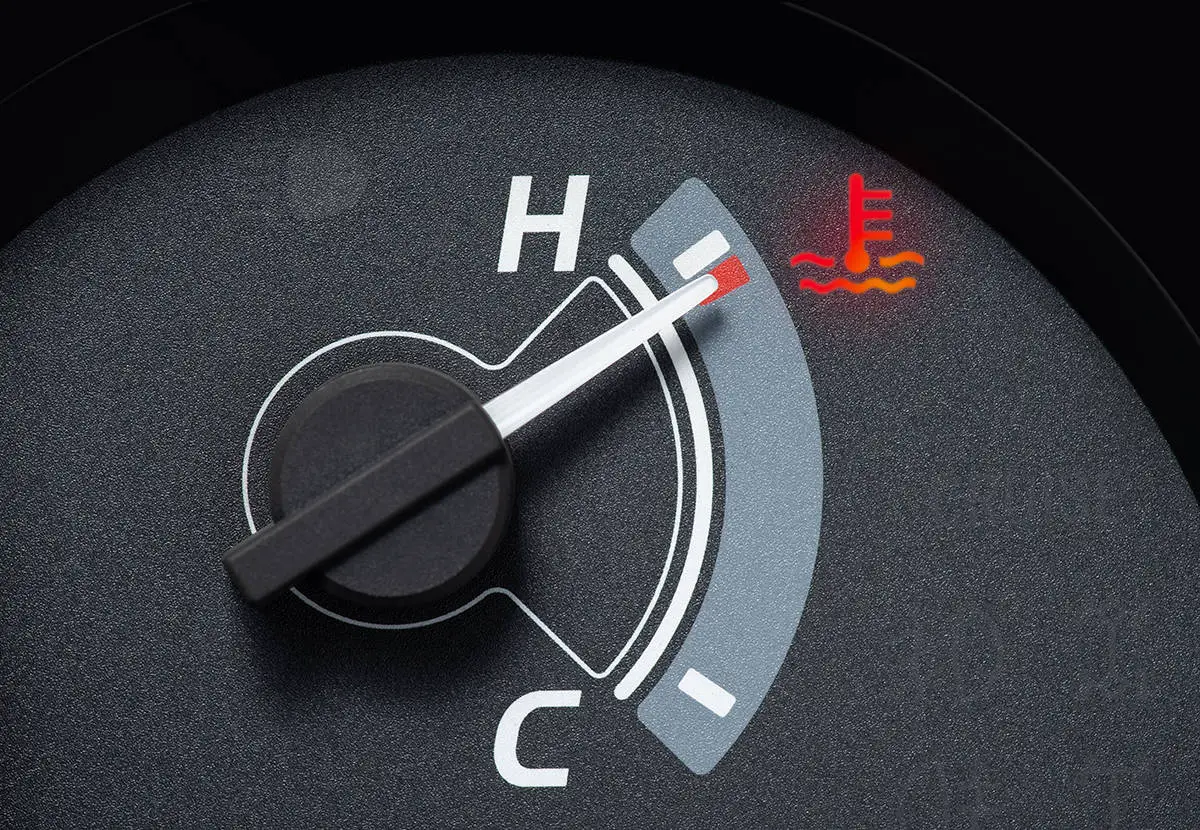

The temperature warning light is a vital indicator in your vehicle’s dashboard that illuminates when the engine is running hotter than it should be. This light is directly related to the transmission’s hot idle engine because if the transmission is overheating, it can cause the engine to run hotter as well.
When the temperature warning light comes on, it’s a clear indication that something is wrong with your vehicle and you should pull over immediately to let the engine cool down. Ignoring this warning can lead to serious damage to your vehicle’s engine and transmission and can even result in complete engine failure.
2. Burning smell
Overheating can cause your transmission fluid to burn, which creates a distinct odor that you may notice. This can happen due to a variety of reasons, such as low fluid levels, old or contaminated fluid, or a malfunctioning cooling system.
3. Slipping gears
When the transmission overheats, it can cause the gears to slip, which can make it difficult to shift smoothly. When the transmission fluid gets too hot, it can cause the gears to slip, which can make it difficult to shift smoothly. Slipping gears can be dangerous as it can lead to a loss of power or control over your vehicle.
4. Delayed engagement
Delayed engagement occurs when there is a delay in your transmission engaging after you shift into gear. This can be caused by a variety of factors, but it’s often related to overheating of the transmission fluid, which can cause it to flow poorly.
When the transmission fluid is overheated, it becomes less viscous and can’t flow through the transmission properly. This can result in a delay in the transmission engaging when you shift gears, which can be frustrating and even dangerous in certain situations.
How to Fix Transmission Hot Idle Engine?
Fixing the transmission hot idle engine is essential to prevent further damage to your vehicle’s transmission and ensure its longevity. There are several steps you can take to fix this issue, depending on the underlying cause.
Check the transmission fluid level
- Park your vehicle on a level surface and apply the parking brake. Leave the engine running.
- Let the engine warm up for a few minutes, then check the transmission fluid level using the dipstick. If the fluid level is low, add more of the correct type of transmission fluid.
- Locate the transmission cooler lines at the transmission. They are usually near the back of the engine area.
- Detach both transmission oil cooler lines at the transmission using a line wrench. Be careful not to lose the thin metal washers. The fittings will leak if these washers are not replaced.
- Use compressed air to blow through the lines and check for blockages.
- If the lines are blocked, replace the transmission cooler. If they are not blocked, check the oil pump, as a failing transmission pump can cause low pressure and overheating.
- Reattach the transmission oil cooler lines using new metal washers.
- Double-check the fluid level using the dipstick, and add more fluid if needed.
Check and fix the transmission cooler

- Check the transmission cooler lines for any leaks or damage. If you notice any issues, replace the lines as needed.
- Check the transmission fluid level and condition. If the fluid level is low, add more of the correct type of transmission fluid. If the fluid is dirty or burnt, have the transmission serviced to replace the fluid and filter
- Inspect the transmission cooler itself for any leaks or damage. If you notice any issues, replace the cooler.
- Consider upgrading to a larger transmission cooler if you frequently tow heavy loads or live in a hot climate. A larger cooler will help to dissipate more heat and keep your transmission running cooler.
Replace the transmission filter.
- Park and elevate the vehicle on a level surface. Turn off the engine and let the transmission cool down for at least 20 minutes to avoid getting burned by hot transmission fluid.
- Locate the transmission pan and remove it with a wrench or socket set. Use a screwdriver to gently break the gasket seal if necessary. Clean the gasket surfaces on both the pan and the transmission housing. Inspect the pan for metal shavings or other signs of internal damage, and then clean it with solvent.
- Remove the old transmission filter and O-ring. The filter contains fluid, so keep the drain pan under the filter to catch any fluid that may spill out. Use a screwdriver to gently pry the filter loose if necessary.
- Install the new filter and O-ring. Ensure that the O-ring is properly seated in the groove and that the filter is securely in place. Some filters may require a new sealant to be applied to the pan before installation.
- Reinstall the transmission pan and tighten the bolts in a criss-cross pattern to ensure a proper seal. Refill the transmission with the recommended amount of fluid and start the engine. Let the engine idle for a few minutes and check for leaks. Add more fluid if necessary and recheck for leaks.
Check and fix electrical issues.
Before attempting any repairs, it’s important to gather as much information about the problem as possible. Determine how the engine is supposed to operate and what symptoms you’re experiencing.
- Turn off the engine and disconnect the battery to avoid any electrical shock or damage.
- Check the wiring harnesses and connectors for any signs of damage, such as corrosion or fraying. Repair or replace any damaged wires or connectors.
- Inspect the fuses and relays related to the transmission and engine control systems. Replace any blown fuses or faulty relays.
- Use a multimeter to test the electrical components related to the transmission and engine control systems, such as the sensors and solenoids. Consult your vehicle manual for the proper testing procedures.
- If any components fail the tests, replace them with new ones. Make sure to use parts that are compatible with your vehicle’s make and model.
- Once all repairs have been made, reconnect the battery and start the engine. Test the transmission and engine control systems to ensure they are functioning properly.







