Newer vehicles have high-tech sensors for almost every function. These sensors ensure top performance, but they aren’t without risk. You should be able to reset the throttle body sensor if you ever have to deal with it.
There are several methods you can try to reset the throttle position sensor, namely:
- Idle the engine
- Push the accelerator
- Drive over 40 mph
- Remove the fuse
- Disconnect the battery
- Drain power from the vehicle
- Use an OBD-II scanner
Today, I’m going to describe what the throttle position sensor is, what can happen when it fails, and how to reset it.
What Is the Throttle Position Sensor?
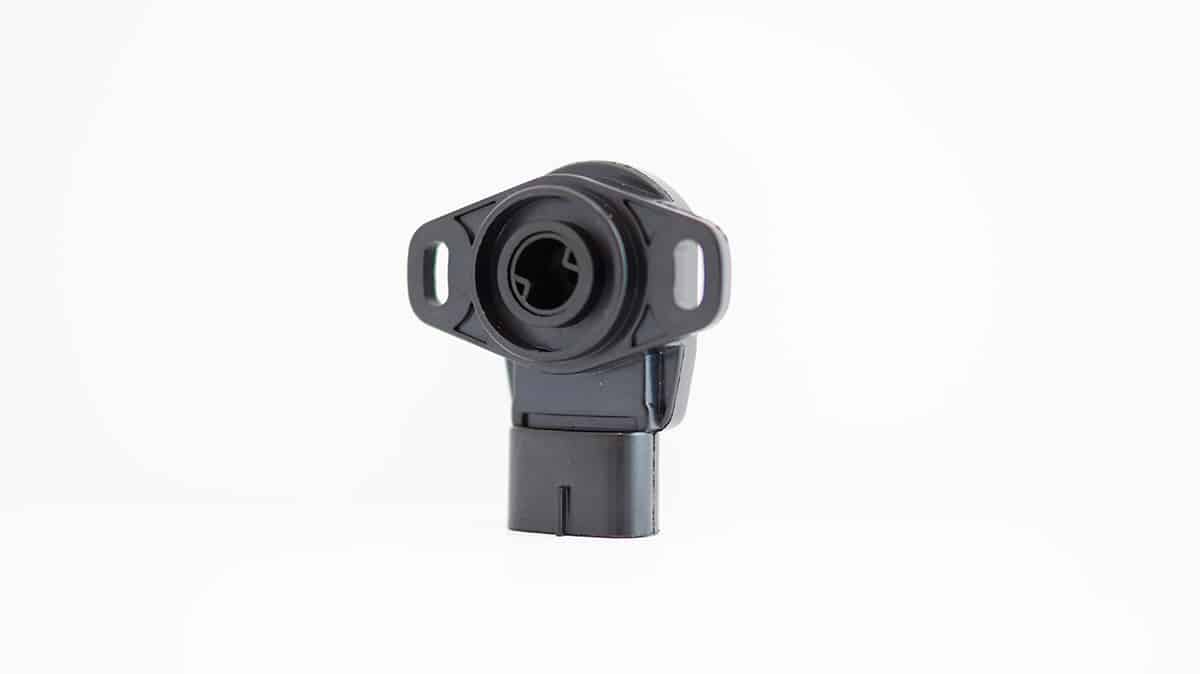

A throttle position sensor is a device that is used to monitor the position of the throttle in an internal combustion engine. The throttle is a valve that controls the flow of air into the engine, and the throttle position sensor is used to measure the degree to which the throttle is open or closed.
The sensor is typically located on the throttle body of the engine, and it consists of a movable arm and a contact point. As the throttle is opened or closed, the arm moves and the contact point makes or breaks an electrical connection. This movement of the arm is translated into an electrical signal, which is sent to the engine control module (ECM).
The ECM uses this signal from the throttle position sensor, along with other inputs such as engine speed and load, to determine the appropriate amount of fuel and air to supply to the engine. This helps to ensure that the engine is running efficiently and smoothly.
What Can Cause the Throttle Position Sensor to Fail?
There are several potential causes for a throttle position sensor to fail. Here are some common causes:
- Wear and tear—Like any other mechanical or electrical component, the throttle position sensor can wear out over time due to normal use. This can cause it to become less accurate or to fail completely.
- Dirt and debris—The throttle position sensor can be damaged or disrupted by dirt, dust, or other debris that gets inside the sensor or on the contact points. This can cause the sensor to malfunction or produce inaccurate readings.
- Water damage—If the throttle position sensor gets wet, it can short out or become damaged. This is particularly a concern if the sensor is located in an area of the engine that is prone to water exposure, such as near the air intake or throttle body.
- Corrosion—If the throttle position sensor is exposed to corrosive substances, such as salt or other chemicals, it can become damaged or malfunction.
- Electrical issues—The throttle position sensor is an electrical component, and it can be affected by issues such as loose connections, damaged wires, or voltage fluctuations.
- Physical damage—If the throttle position sensor is subjected to physical trauma, such as being hit by a rock or other debris, it can become damaged and fail.
- Improper installation—If the throttle position sensor is not installed correctly, it can fail prematurely or produce inaccurate readings.
What Happens When the Throttle Position Sensor Fails?
These are a few major symptoms of a failing throttle position sensor.
- Acceleration problems— Problems with acceleration are almost inevitable if your throttle body is broken. This means that you may not be able to accelerate to your desired speed even though it feels as though you are pressing the accelerator pedal to the floor properly. The car may feel like it’s in low gear even when the accelerator is fully depressed.
- Power problems— A malfunctioning throttle body can cause acceleration issues as well as sudden, unexpected motion. This can also negatively impact your vehicle’s milage.
- Rough idling or stalls— There should be no change in throttle position sensors when the vehicle is at rest. It takes a certain amount of gas for the car to stay at idle; if it isn’t doing so, you may need to adjust the throttle.
- Transmission shifting problems— If your transmission position sensor is malfunctioning, shifting gears will be more difficult than usual. If you notice that, even when you floor the accelerator pedal, switching to higher gears makes the car feel like it’s still in a low gear.
- Check engine light— If your car exhibits any of the signs mentioned above, in addition to the check engine light coming on, the problem is most likely a faulty throttle position sensor.
How to Reset Throttle Position Sensor
Before taking your vehicle to a professional mechanic to fix a failing throttle position sensor, there are a few things you can do to reset it.
1. Idle the engine
Idling the engine is not a 100% proven way to reset a throttle position sensor, but it’s worth doing to figure out whether the sensor really is faulty.
- Turn the engine on.
- Wait for 5 minutes.
- Turn the engine off.
- Wait for 10 minutes before turning the engine back on.
2. Push the accelerator
If idling the engine doesn’t work, try pushing on the accelerator. Here’s how you do it.
- Turn your car on but do not start the engine. If you have a keyless start button, press it quickly but not long enough to start the engine.
- Slam on the accelerator for 15 to 20 seconds.
- Slowly release the accelerator.
- Turn the car off.
- Turn the engine on.
3. Drive over 40 mph
In rare instances, simply driving your car around can reset the throttle position sensor. The secret is to maintain a speed of 40 mph for a couple of minutes to successfully reset the sensor.
After driving around at 40 mph for about 10 minutes, pull over, put your car in park, and let it idle for about 5 minutes. Redo the process 2 or 3 more times to reset the throttle position sensor.
4. Remove the fuse
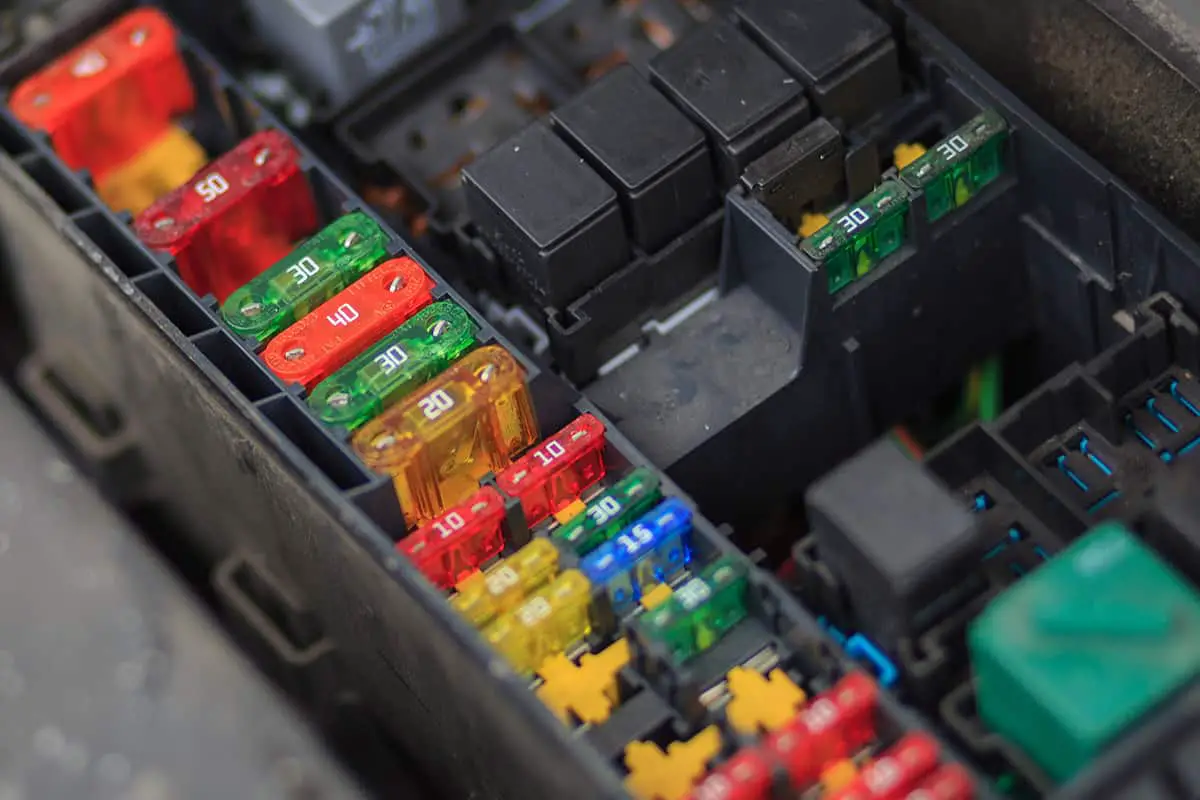

The throttle position sensor is an electrical component in your vehicle. As such, the electricity is delivered via a fuse, and you can disconnect the fuse to cut power to the sensor.
- Locate the fuse by consulting your car owner’s manual.
- Disconnect the fuse for 10 to 15 minutes.
- Reconnect the fuse.
- Start the engine.
Please note that any other electronics connected to the same fuse will be depowered, meaning that you may need to the clocks in your car and infotainment system.
5. Disconnect the battery
If the throttle position sensor is experiencing minor electrical problems, you can usually resolve it by disconnecting the car battery.
- Disconnect the negative terminal and positive terminal in that order.
- Wait for 5 minutes.
- Reconnect the terminals (positive before negative).
- Turn the engine on.
6. Drain power from the vehicle
While disconnecting the car’s battery will stop it from powering electronics, that doesn’t mean there won’t be lingering electricity in the system. To drain the power from your car, simply disconnect the battery following the steps above, but let your car rest for 10 to 30 minutes before reconnecting the battery.
7. Use an OBD-II scanner
An OBD-II scanner, also known as an OBD-II diagnostic tool, is a device used to read and interpret diagnostic data stored in the OBD-II system of a vehicle. The scanner is connected to the vehicle’s diagnostic port, which is typically located on the driver’s side of the dashboard.
The OBD-II scanner can retrieve and display diagnostic codes and other information from the vehicle’s onboard computer, which is useful for diagnosing and resolving issues with the engine, transmission, and other systems.
If you do not own an OBD-II scanner, or if you don’t know how to operate one (this video guide can help you out), consider taking your vehicle to a mechanic or the authorized dealership to resolve your throttle position sensor problem.