Catalytic converters, the essential devices in vehicles that significantly reduce harmful emissions, hold substantial value even after they’ve outlived their usefulness. This is largely due to the precious metals they contain, like platinum, palladium, and rhodium. These metals have high demand and limited supply in various industries, including the automotive sector, leading to competitive market prices.
In the realm of scrap metal, catalytic converters can fetch prices ranging from $50 to over $250, primarily driven by the type and quantity of precious metals they contain, such as platinum, palladium, and rhodium. Note that market fluctuations can influence these prices significantly.
This comprehensive guide aims to delve into the intriguing world of catalytic converter scrap prices. We will explore what these devices are made of, why they’re valuable, how their scrap prices are determined, and where you can sell them.
The Inner Workings of a Catalytic Converter
A catalytic converter is designed to neutralize harmful emissions. Understanding how it works can shed light on its value in the scrap market.
Construction of Catalytic Converters
Catalytic converters are compact devices typically housed in a stainless steel casing. The main component inside is a honeycomb-like structure called a substrate, made from ceramic or sometimes metal.
This substrate is coated with a washcoat that provides a large surface area for catalytic reactions. The washcoat is where the magic happens, as it’s impregnated with precious metals such as platinum, palladium, and rhodium.
Catalytic Converter Materials
Platinum, palladium, and rhodium are the stars of the show in catalytic converters. They serve as catalysts, substances that speed up chemical reactions without getting consumed in the process.
- Platinum is used in both diesel and gasoline engines, but it’s more prevalent in the latter. It’s instrumental in controlling the conversion of carbon monoxide (CO) and unburnt hydrocarbons (HC) into carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O).
- Palladium is the primary catalyst in gasoline engines, aiding in the oxidation of CO and HC.
- Rhodium, the most expensive of the three, plays a critical role in converting nitrogen oxides (NOx), a major contributor to smog and acid rain, into harmless nitrogen (N2) and oxygen (O2).
While these metals comprise only a small fraction of the converter’s weight, their scarcity and high market value drive the worth of catalytic converter scrap.
The Value of Catalytic Converter Scrap
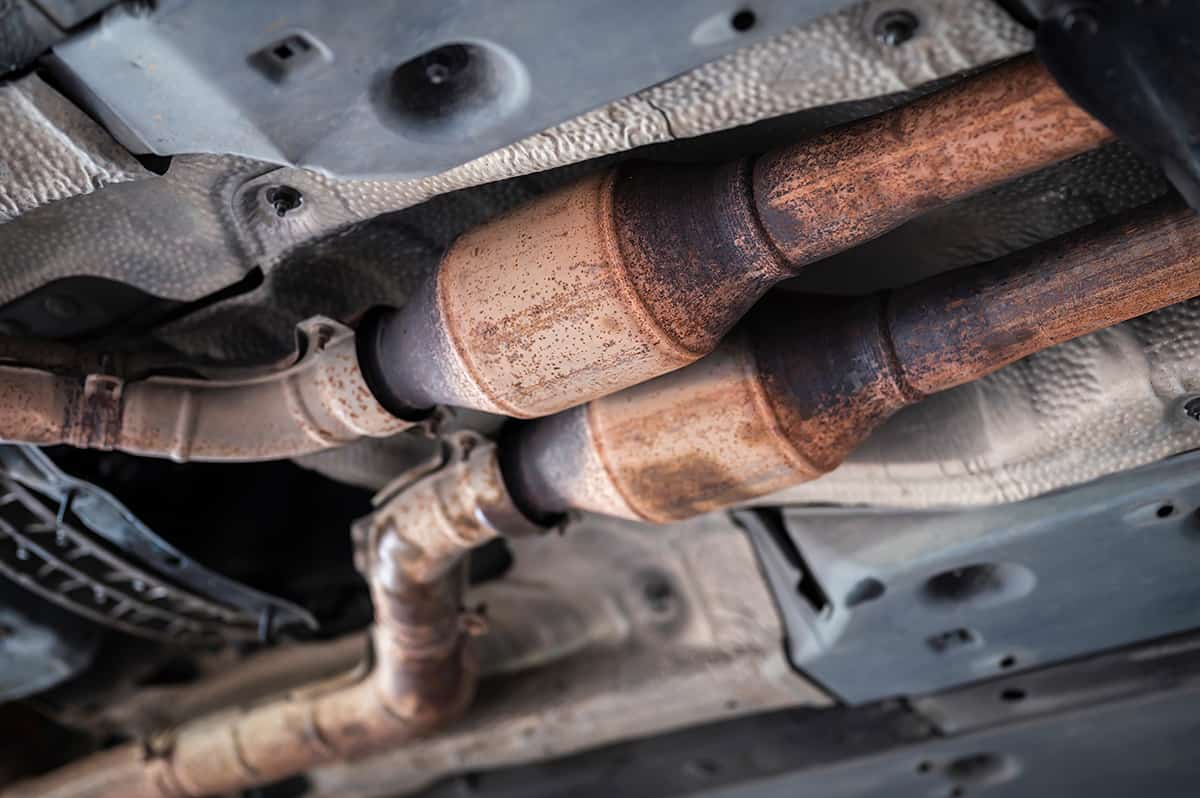

Catalytic converters are installed in the exhaust system of a vehicle between the engine and the muffler. Their role is to cleanse the exhaust gases of harmful pollutants before they’re released into the environment.
Once the engine burns the air-fuel mixture to produce power, it also creates exhaust gases that contain harmful substances like CO, HC, and NOx. These gases flow into the catalytic converter, where they come into contact with the precious metal-coated substrate. Here, the catalysts trigger chemical reactions that convert these pollutants into less harmful substances: CO2, H2O, N2, and O2.
The effectiveness of a catalytic converter depends on its operating temperature and the condition of the engine. An efficient engine produces an optimal air-fuel mixture for the catalytic converter to do its job effectively. Hence, regular engine maintenance can prolong the life of your catalytic converter.
Catalytic Converter Scrap Price List
Catalytic converter scrap prices fluctuate with the market rates of platinum, palladium, and rhodium. These metals, used in small quantities within each converter, are highly valuable due to their rarity and wide industrial application. Therefore, when the market rates of these metals increase, the scrap prices also rise.
Most catalytic converter buyers provide a price list, often available on their website, indicating the amount they’re willing to pay for specific converters. These lists are usually organized by part numbers, also known as catalytic converter codes. The higher the precious metal content, the more valuable the converter.
Here is a list from YS Catalytic Recycling, one of the largest catalytic converter buyers in New York:
| Catalytic Converters | Prices |
| AFTERMARKET | $16 |
| AIRTUBE | $64 |
| BL/THICK PIPE | $203 |
| CAMRY | $84 |
| DIESEL | $13 |
| DOMESTIC FOIL | $16 /lb. |
| ELITE/PIG HI | $713 |
| EXOTIC SMALL | $346 |
| EXOTIC/FAT SLANT LOW | $395 |
| FOREIGN FOIL | $19 /lb. |
| FOREIGN LARGE | $231 |
| FOREIGN MEDIUM | $187 |
| FOREIGN PRE/HG PRE | $74 |
| FOREIGN SMALL | $148 |
| GM | $166 |
| GM AC/BL THIN PIPE | $92 |
| GM MEDIUM (4DOT) | $129 |
| HIGH GRADE DOMESTIC | $142 |
| JEEP | $140 |
| JUMBO BEAD | $85 |
| LOW GRADE FOREIGN | $104 |
| LOW PRE | $32 |
| O2 SLANT | $324 |
| O2 STRAIGHT | $485 |
| REG PRE | $49 |
| REGULAR BEAD | $32 |
| SE 5-LINE | $166 |
| SE 6-LINE | $218 |
| SE HIGH GRADE | $403 |
| SE LOW (10LINE,13LINE) | $89 |
| SE MEDIUM/SMOOTH | $187 |
| SMALL FLOW | $72 |
| STANDARD DOMESTIC | $111 |
| SUPER EXOTIC/FAT SLANT HI | $511 |
| TORPEDO 3B | $319 |
| TORPEDO 4B (round/oval) | $208 |
| TORPEDO HI | $653 |
| XBODY | $206 |
| XL FOREIGN | $297 |
Note: The prices on this list are subject to change. You should check out YS Catalytic Recycling’s price list for the latest prices.
Different Types of Catalytic Converters
The type of catalytic converter plays a significant role in determining its scrap value. There are three main types:
- Two-way converters, found mostly in older model vehicles, contain both platinum and palladium.
- Three-way converters are most commonly found in modern vehicles and contain all three precious metals: platinum, palladium, and rhodium.
- Diesel Oxidation Catalysts (DOCs) are used in diesel vehicles and contain platinum and palladium.
Catalytic Converter Codes
Each catalytic converter has a unique code etched or stamped on its structure, reflecting its manufacturer and model. This code allows buyers to identify the type and quantity of precious metals within the converter. Consequently, knowing your catalytic converter’s code is crucial in estimating its value accurately.
Some buyers even provide online tools to input your code and get an instant price quote. Remember that these are estimates and the actual payout can vary based on the current market conditions and the physical condition of your converter.
Selling Catalytic Converter Scrap
When it comes to selling catalytic converter scrap, having a strategy can significantly impact the payout you receive. This section provides information on the best places to sell your scrap and important legal considerations.
Where to Sell Catalytic Converter Scrap
There are multiple avenues to sell your catalytic converter scrap. Here are the most common ones:
- Scrap Yards: These local businesses buy all kinds of metal scrap, including catalytic converters. However, their offer might not reflect the actual value of the precious metals within the converter due to their generalist nature.
- Specialized Catalytic Converter Buyers: These businesses focus solely on buying used or damaged catalytic converters. They are more likely to offer better prices as they understand the real value of the metals inside.
- Online Marketplaces: Websites like eBay and Craigslist can be useful platforms to sell your scrap. However, be cautious of potential scams and understand shipping and transaction fees.
- Direct to Refiners: Selling directly to metal refiners can net you the highest profits, as you bypass any middlemen. However, they usually deal in bulk, which might not be suitable for individual sellers.
Legal Considerations
In many places, it’s illegal to sell used catalytic converters unless they’ve been decertified, which usually involves separating the casing from the inner materials.
Additionally, some states require documentation proving lawful possession of the catalytic converter. This can include invoices or receipts showing it was replaced during legitimate vehicle repairs. Always check the laws in your area before proceeding.
Tips and Strategies for Getting the Best Scrap Prices
Here are some tips to help you get the best price for your catalytic converter scrap:
- Know Your Converter: Understand the type of converter you have and the metals it contains. This information can be found by identifying the converter’s code.
- Monitor Metal Prices: The prices of platinum, palladium, and rhodium fluctuate based on market demand and supply. Keep an eye on these prices to choose the best time to sell.
- Consider the Condition: Converters in better condition usually fetch higher prices. Avoid damaging the converter when removing it from the vehicle.
FAQs
1. How can I find the code on my catalytic converter?
The code on a catalytic converter, also known as the part number, is typically found on the shell of the converter. It’s often etched or stamped into the metal. Depending on the make and model, it could be on the side, top, or bottom.
The code usually consists of letters and numbers. It may be difficult to see due to grime or rust, so you might need to clean the surface or use a flashlight to make it visible. If you can’t find the code, it might be best to consult with a professional or the converter manufacturer for assistance.
2. Is it legal to sell catalytic converter scrap?
The legality of selling catalytic converter scrap varies by region, so it’s essential to check local laws and regulations. In many places, you can legally sell scrap catalytic converters if they’ve been decertified, which usually means the casing has been separated from the internal materials.
Certain jurisdictions also require proof of lawful possession, like an invoice or receipt showing the converter was replaced during legitimate vehicle repair work. Always ensure compliance with local laws to avoid penalties or legal trouble.