Your car is like a giant puzzle with many parts, and one key piece is the oxygen sensor. This tiny device tells your car’s computer how much fuel to use for the engine to run smoothly and efficiently. When it works well, you might not notice it. But when it starts to fail, it can cause a bunch of problems and might even harm the environment.
Symptoms of a bad or failing oxygen sensor include:
- Your check engine light comes on
- Your car uses more gas than usual
- Your engine runs rough or misfires
- You notice a strange smell from the exhaust
- Your car fails an emissions test
In this guide, we’ll delve deeper into these symptoms, discuss where and how you can replace a faulty oxygen sensor, and estimate the costs involved.
Introduction to Oxygen Sensors
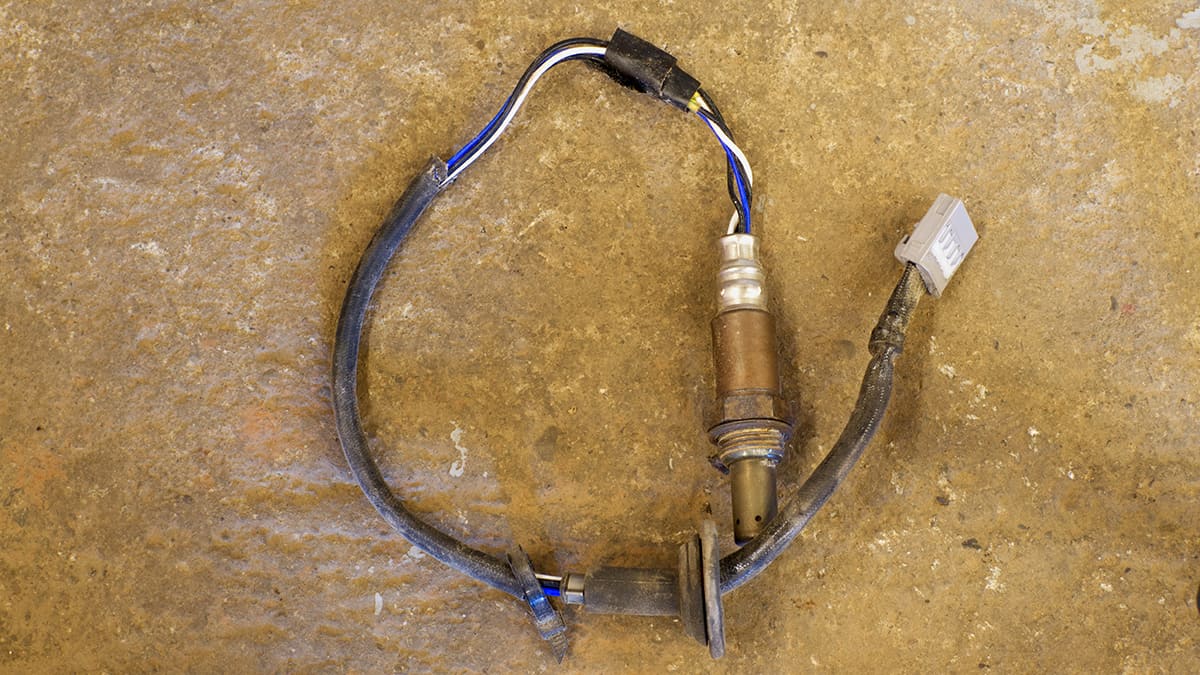

In your car, the oxygen sensor, a vital component, ensures the engine gets just the right amount.
The role of an oxygen sensor
The oxygen sensor sits in your car’s exhaust system and measures the amount of oxygen in the gases that come out of your engine.
Why is this important? Your car needs to burn fuel to move, and for optimal burning, it needs a precise mixture of fuel and oxygen. Too much or too little oxygen can cause problems, including reduced fuel efficiency and increased pollution.
The information from the oxygen sensor is sent to the car’s computer, also known as the engine control unit (ECU). The ECU uses this information to adjust how much fuel is sent to the engine, striving to maintain the perfect balance for efficient combustion. This is crucial for both the performance of your vehicle and for minimizing its impact on the environment.
How oxygen sensors work
Inside the sensor, there are two chambers, each filled with different amounts of oxygen. One chamber is exposed to the exhaust gases from your engine (which may have too much or too little oxygen), while the other is exposed to the outside air (which has a consistent amount of oxygen). The difference in oxygen levels between the two chambers generates a voltage.
The sensor then sends this voltage as a signal to the ECU. If the voltage is high, it means there’s not enough oxygen in your exhaust, and your engine is running “rich” with too much fuel. If the voltage is low, there’s too much oxygen, and your engine is running “lean,” with not enough fuel. The ECU adjusts the fuel input to the engine accordingly.
Recognizing the Symptoms of a Bad or Failing Oxygen Sensor
Your car can show signs when its oxygen sensor isn’t functioning properly. Identifying these symptoms early can help you prevent bigger problems and costly repairs.
1. Check engine light
Your car’s computer keeps track of all its components. If the oxygen sensor is failing, the computer will trigger the check engine light on your dashboard. However, many things can cause this light to turn on, so a light alone doesn’t mean your oxygen sensor is the culprit.
2. Reduced fuel economy
A failing oxygen sensor can’t provide accurate information to your car’s computer. As a result, the computer might supply too much or too little fuel to the engine. This imbalance can make your car consume more fuel than usual, reducing its gas mileage. If you notice that you’re filling up the gas tank more frequently, your oxygen sensor might be at fault.
3. Rough idle or misfires
When the balance of fuel and oxygen in your engine isn’t just right, it may cause your car to vibrate or shake while idling (when your car is turned on but not moving). It might also cause the engine to misfire, which feels like a sudden jerk or “skip” while driving. These issues often indicate a problem with the oxygen sensor.
4. Strange exhaust smells
If the exhaust coming from your car has a stronger smell than usual, it could be a sign that your oxygen sensor is failing. A faulty sensor might cause the engine to burn more fuel than it should, resulting in a heavy, gasoline-like odor from the exhaust.
5. Failed emissions test
Many places require cars to pass an emission test as part of their environmental regulations. This test checks the amount of pollutants that your car releases into the air. If your oxygen sensor isn’t working correctly, your car might burn more fuel than necessary, leading to increased emissions. As a result, your vehicle could fail its emission test.
Deciding Where to Replace Your Oxygen Sensor
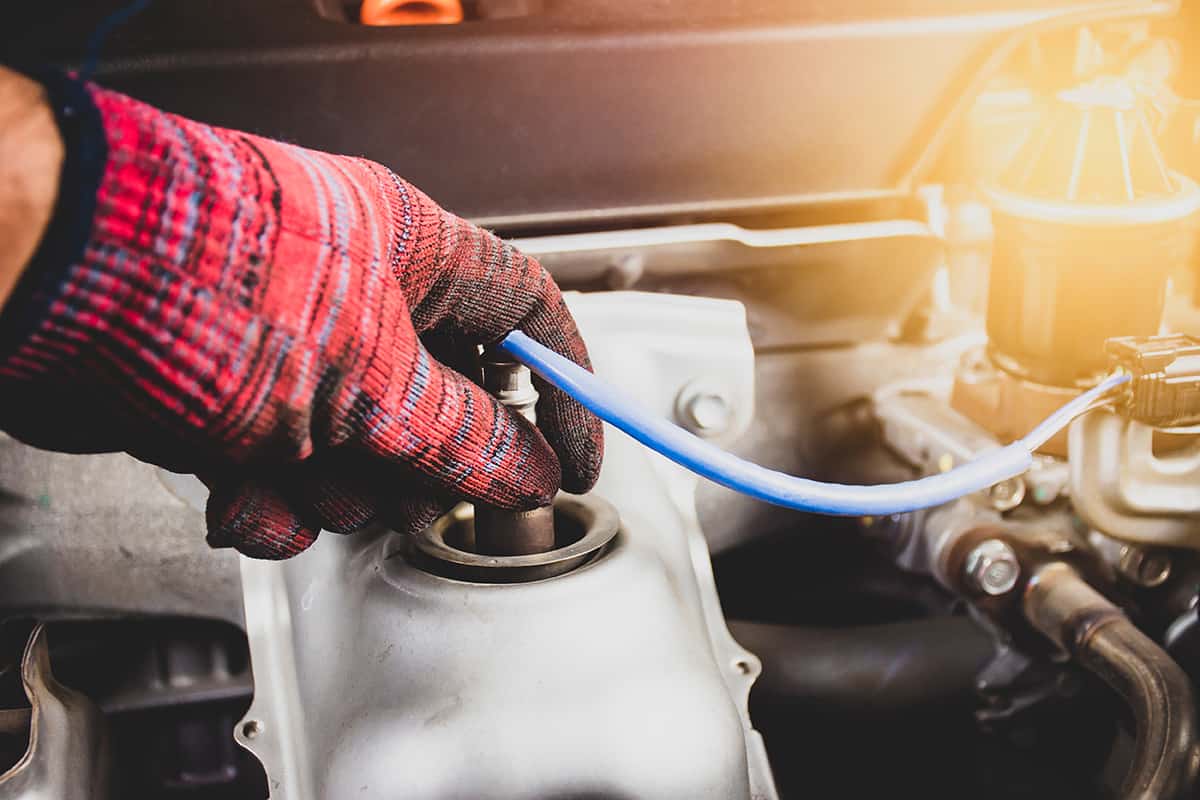

If your car’s oxygen sensor is failing, you’ll need to replace it to keep your car running smoothly. But where should you get it replaced? Let’s look at some options.
1. Dealership service centers
Getting your oxygen sensor replaced at a dealership service center is one option. Dealerships have trained technicians who know your car’s make and model well. They’ll use official parts, so you can be confident in their quality.
But dealership services usually cost more than other options. While you’re paying for expertise and high-quality parts, it might not be the best choice if you’re trying to save money.
2. Independent auto repair shops
Independent auto repair shops can also replace your oxygen sensor. These are smaller businesses not tied to a specific car brand. Prices at these shops can be lower than at dealerships, but the quality of service and parts can vary.
Some shops have highly skilled technicians and use high-quality parts, while others might not. When choosing an independent shop, do some research. Check reviews and ask for recommendations to find a reputable place.
3. DIY replacement
If you’re handy with tools and have some knowledge about cars, you might consider replacing the oxygen sensor yourself. You’ll need to buy the right sensor for your car, which you can usually find online or at an auto parts store. Replacing the sensor can be a bit tricky, depending on its location in your car. You’ll also need certain tools, like an oxygen sensor wrench.
This option can save you money on labor costs, but it’s not recommended unless you’re confident in your abilities. Doing it wrong could cause more problems down the line.
Estimating the Costs of Oxygen Sensor Replacement
Replacing your car’s oxygen sensor comes with a cost. Understanding what affects this cost and comparing prices can help you make the best decision.
Factors Affecting Replacement Costs
Several things can influence how much you’ll need to pay to replace your oxygen sensor. One is the type of sensor your car uses. Some cars use a single-wire sensor, while others use a four-wire sensor. Generally, the more wires a sensor has, the more it costs.
The brand of the sensor can also affect the price. Some brands are known for their quality and durability but come with a higher price tag.
Labor costs also play a role. These costs can depend on where you choose to have the work done and how complex the replacement process is for your specific car. For instance, if the sensor is hard to reach, it might take more time and increase labor costs.
Dealership vs. Independent Shop vs. DIY
The place where you choose to replace your oxygen sensor can significantly influence the overall cost.
At a dealership, you might pay more, but you’re paying for their expertise and the assurance of quality parts. Independent shops usually offer lower rates than dealerships, but the quality can vary.
If you’re considering a DIY replacement, you’ll mainly pay for the new sensor and any tools you might need. This can be the cheapest option, but only if you’re confident in your skills. If you make a mistake, you might end up paying more in the long run.