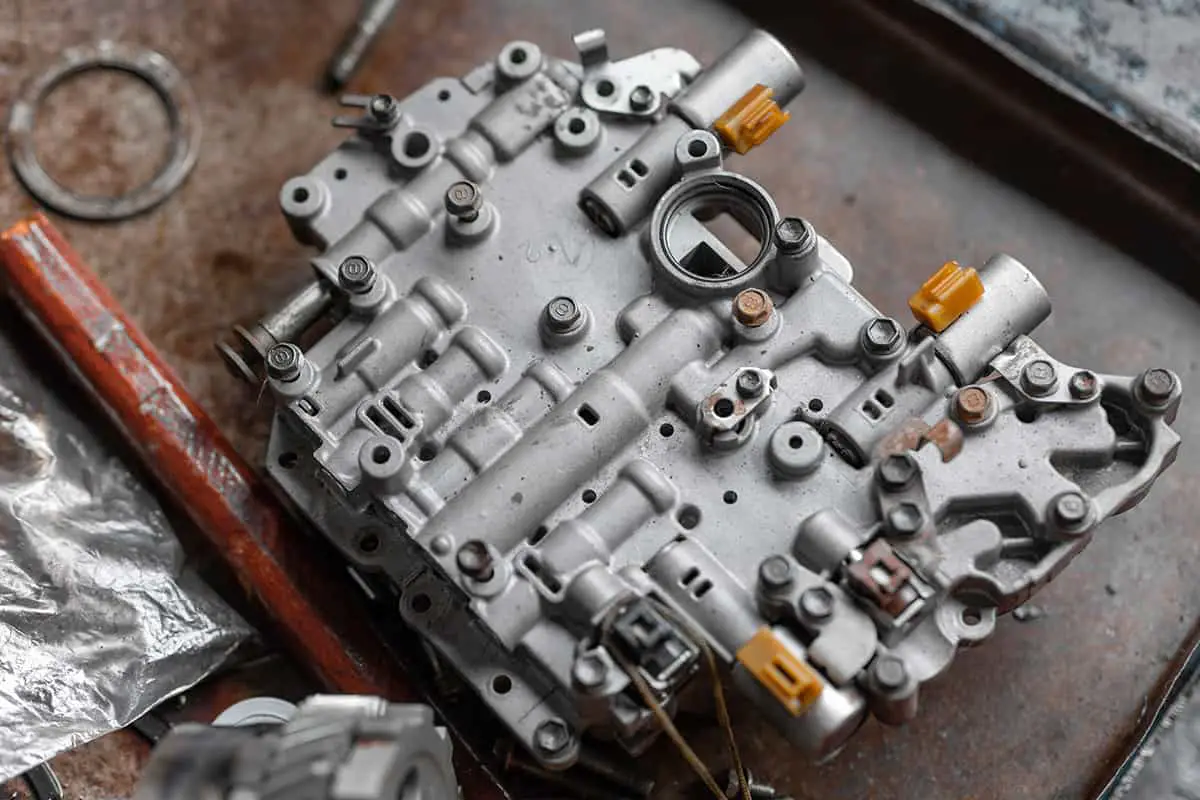
If you’re experiencing transmission issues with your vehicle, one possible culprit could be a malfunctioning Transmission Control Module (TCM). This critical component is responsible for regulating the transmission’s shifting and ensuring smooth acceleration and deceleration. If you suspect that your TCM may be the problem, the first step in addressing the issue is to locate it within your vehicle.
In manual cars, the TCM is typically located inside the car’s engine control module. On the other hand, in cars with Continuously Variable Transmission (CVT), the TCM is often integrated into the valve body of the transmission itself.
In this blog post, we’ll discuss how to locate the TCM and what you can do when dealing with a problematic TCM.
What Is the Transmission Control Module (TCM)?
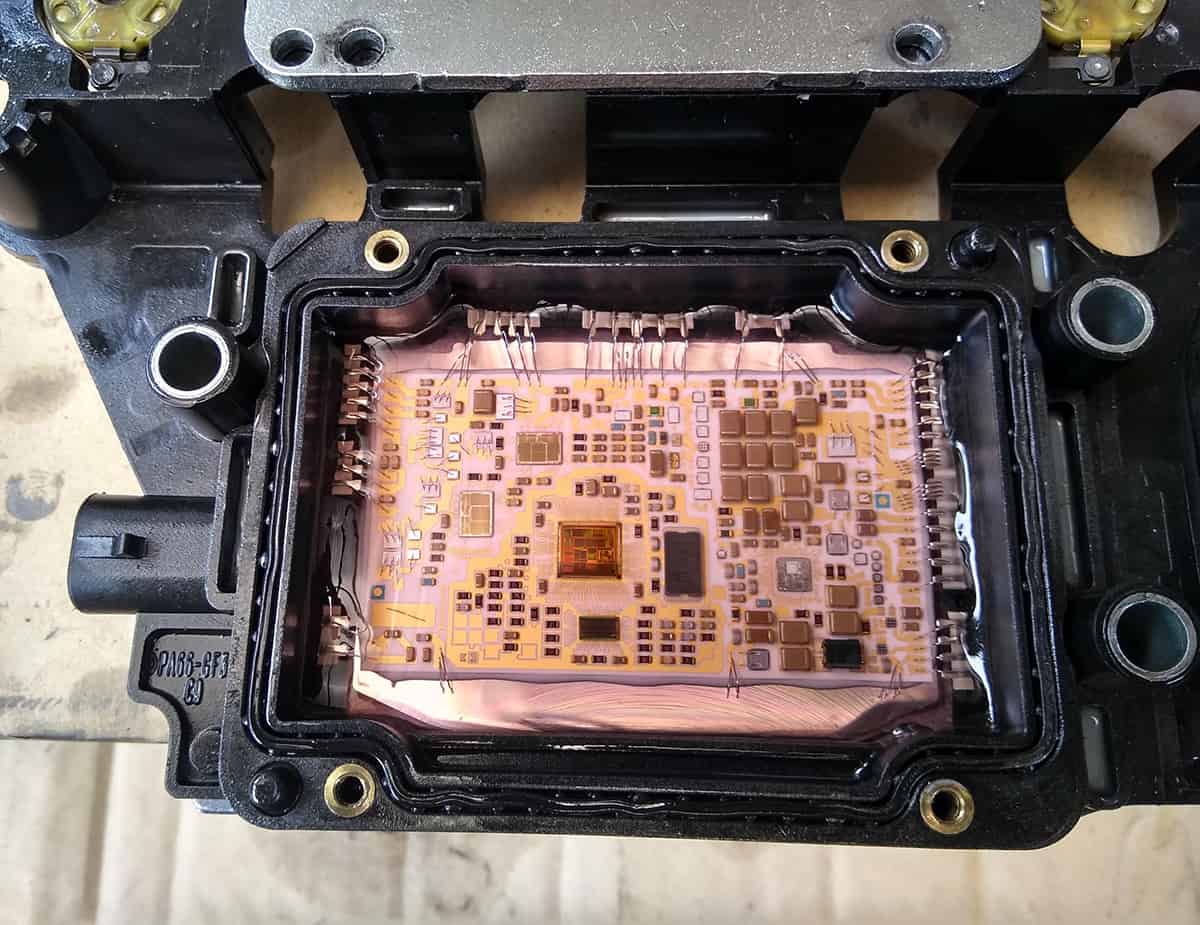

The TCM is a crucial component of modern vehicles, responsible for managing and optimizing the transmission system. It is an electronic device that processes information from various sensors in the vehicle to ensure smooth gear shifting, optimal fuel efficiency, and overall driving performance.
At the heart of the TCM’s function is its ability to receive and interpret signals from different vehicle sensors, such as the throttle position sensor, vehicle speed sensor, and transmission fluid temperature sensor. By processing this information in real-time, the TCM can determine the best moment to shift gears, engage the torque converter lock-up, and manage other transmission-related functions.
In automatic transmissions, the TCM is particularly vital, as it controls the hydraulic pressure applied to the clutches and bands responsible for gear changes. In manual transmissions, it may have a more limited role, such as managing the overdrive or cruise control features. For vehicles with continuously variable transmissions (CVTs), the TCM plays a key role in maintaining the appropriate gear ratio for varying driving conditions.
As vehicles become more advanced, the TCM often becomes integrated with other control modules, such as the engine control module (ECM) or the body control module (BCM). This interconnectedness allows for improved communication and coordination between various vehicle systems, ultimately contributing to a more efficient and responsive driving experience.
Common Transmission Control Module Functions
The TCM is responsible for numerous functions that ensure the seamless operation of the transmission system. Its primary roles include:
1. Gear shifting
The TCM determines the optimal timing and speed for gear shifts, enabling smooth transitions and maintaining peak engine performance.
2. Torque converter control
The TCM manages the torque converter’s lock-up, which affects vehicle acceleration and fuel efficiency by allowing or preventing slippage between the engine and transmission.
3. Overdrive and cruise control
In vehicles with manual transmissions, the TCM may regulate overdrive, a higher gear ratio for efficient highway cruising, and cruise control, which maintains a constant speed without manual throttle input.
Locating the TCM in Automatic Transmissions
The location of the TCM can vary significantly between different vehicles, depending on the make, model, and year. In most cases, the TCM is mounted in the engine bay, either on the firewall or near the fender. However, some manufacturers may place the TCM inside the passenger cabin, under the dashboard, or within the center console.
Locating the TCM in Manual Transmissions
In vehicles with manual transmissions, the TCM often has a less prominent role, primarily focusing on functions such as overdrive and cruise control. As a result, the location of the TCM may differ from that in automatic transmissions. Similar to automatic transmission vehicles, the TCM in manual transmission vehicles can be found in the engine bay or inside the passenger cabin.
Locating the TCM in CVT Transmissions
CVTs are unique in that they don’t have a fixed set of gears but rather use a belt or chain system to provide an infinite range of gear ratios. In CVT-equipped vehicles, the TCM plays a crucial role in maintaining the optimal gear ratio for varying driving conditions.
The TCM in CVT transmissions is typically located in the engine bay, near the transmission itself. However, it can also be found inside the passenger cabin, under the dashboard, or within the center console.
Importance of TCM Location
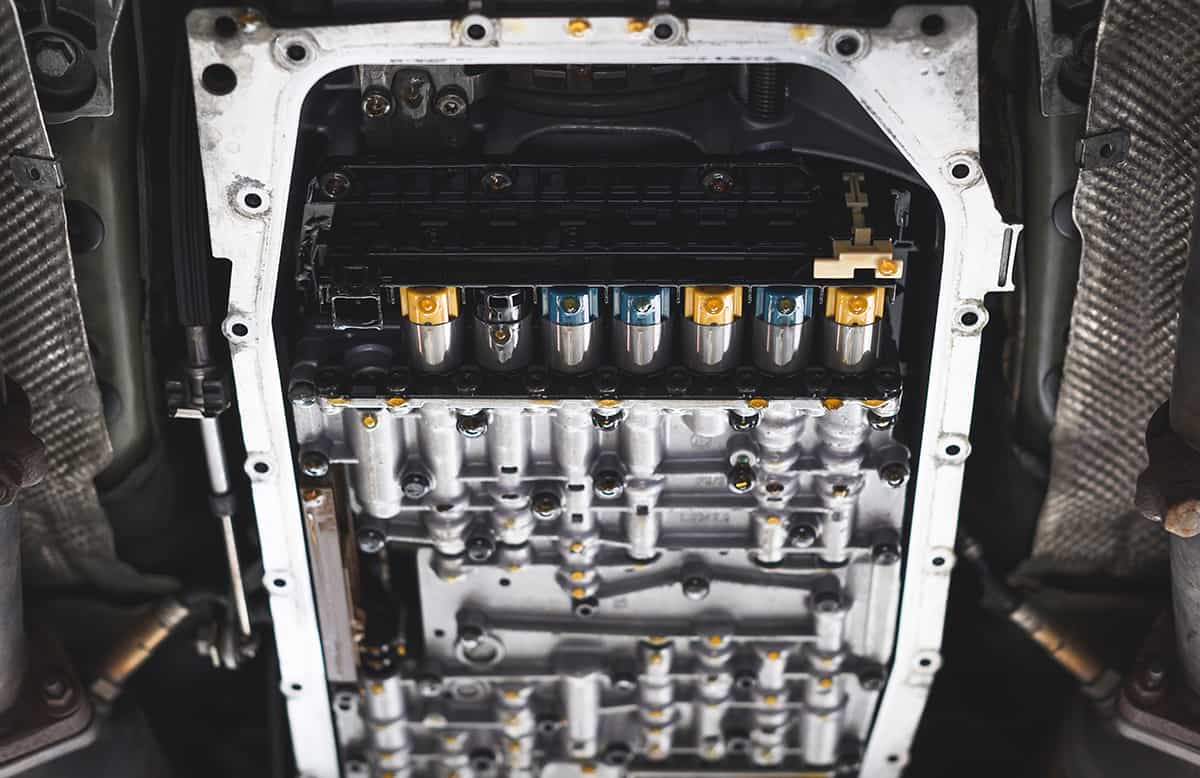

The TCM location is vital for several reasons. First and foremost, it must be protected from heat and moisture, which can cause damage to its electronic components and lead to performance issues or failure. By placing the TCM in a secure and insulated location, manufacturers can reduce the likelihood of these issues.
Accessibility is another critical factor in TCM location. To facilitate easy access for maintenance, diagnostics, and potential replacement, the TCM must be situated in a place where technicians and vehicle owners can reach it without too much difficulty. This consideration helps ensure that any necessary repairs or updates can be performed efficiently and effectively.
Common TCM Issues
The TCM can experience various issues, which may result in symptoms like erratic gear shifting, poor fuel efficiency, or even transmission failure. Some common problems include:
- Corroded or damaged connectors—Moisture, dirt, and debris can cause the connectors to corrode, affecting the communication between the TCM and other vehicle components.
- Faulty or failing sensors—If a sensor provides inaccurate information to the TCM, it may result in incorrect gear shifting or other transmission issues.
- Software glitches—Occasionally, the software in the TCM may develop faults that impact the module’s performance.
- Internal component failure—Over time, the TCM’s internal components may wear out or fail, leading to a range of transmission problems.
TCM Troubleshooting and Maintenance
Regular maintenance and prompt troubleshooting are essential for ensuring the longevity and performance of your vehicle’s TCM. To keep it in top condition, consider the following tips:
- Regular check-ups—Have a professional technician inspect your vehicle’s transmission system, including the TCM, during routine maintenance visits. This will help identify any potential issues before they become serious problems.
- Diagnostic tools—Invest in a quality scan tool or code reader to access diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and pinpoint any issues with the TCM or other vehicle components.
- Cleaning and replacement—If you suspect your TCM is experiencing connectivity issues due to dirt or corrosion, carefully clean the connectors and inspect them for damage. If necessary, replace any damaged connectors to ensure proper communication between the TCM and other vehicle systems.
- Professional assistance—If you’re unsure how to diagnose or address a TCM issue, seek the help of a qualified technician to ensure the problem is resolved correctly and safely.
FAQs
1. How do I know if my TCM is failing?
Signs of a failing TCM may include erratic or harsh gear shifting, slipping gears, poor fuel efficiency, and delayed transmission response. In some cases, you may also experience the “check engine” or “transmission” warning lights on your dashboard. To confirm a TCM issue, use a scan tool or code reader to access diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) related to the transmission system.
2. Can I replace my TCM at home?
Replacing a TCM at home is possible for experienced DIYers with the necessary tools and knowledge. However, it’s essential to follow the correct procedures, use appropriate safety measures, and consult your vehicle’s repair manual. If you’re unsure about your skills, it’s safer to seek professional help.
3. What are the common reasons for TCM failure?
Common reasons for TCM failure include corroded or damaged connectors, faulty or failing sensors, software glitches, and internal component failure. Exposure to heat, moisture, and debris can also contribute to TCM issues, emphasizing the importance of proper maintenance and protection.
4. How often should I have my TCM checked?
It’s a good idea to have your TCM checked during regular maintenance visits, typically every 30,000 to 60,000 miles, depending on your vehicle’s make and model. Consult your owner’s manual for the recommended maintenance schedule. If you notice any signs of transmission problems, have your TCM inspected sooner.