The catalytic converter contributes significantly to the reduction of harmful emissions. This small but mighty device facilitates chemical reactions that transform dangerous pollutants into less harmful substances, thereby promoting a cleaner environment. Despite its importance, many people, including some truck owners, are not entirely clear on its location and function.
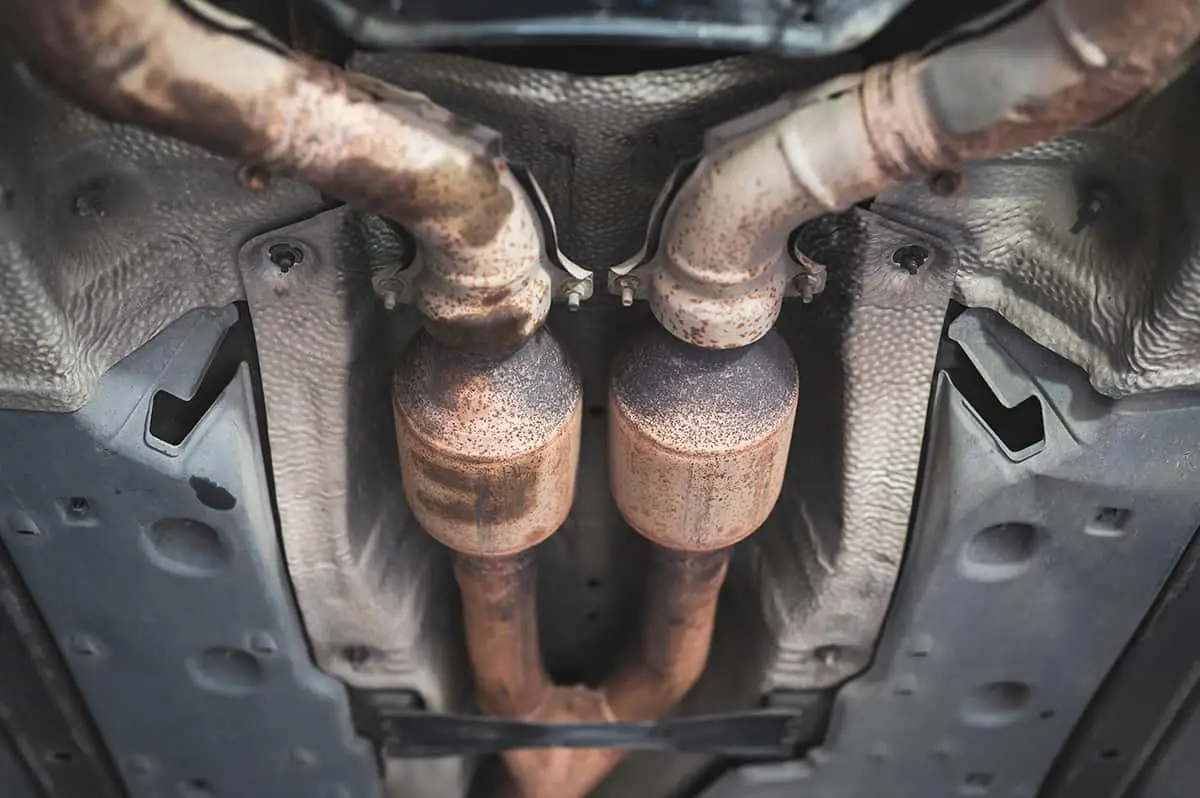
In most semi trucks, the catalytic converter is located within the exhaust system, usually positioned under the vehicle, between the engine and the muffler.
This article will take a closer look at the specificities of a semi truck’s catalytic converter, explaining its strategic positioning and the impact this has on its functionality.
The Catalytic Converter Explained

A catalytic converter, a key player in the exhaust system of a semi-truck, is an emissions-control device that neutralizes harmful gasses before they exit the vehicle. Comprised of precious metals like platinum, palladium, and rhodium, this device triggers chemical reactions that transform harmful substances into less hazardous emissions.
A catalytic converter is a metal canister installed in the exhaust system of a semi truck, serving as a site for essential chemical reactions. When the engine combusts fuel to power the vehicle, it releases several toxic gasses, including carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, and hydrocarbons. These gasses are harmful both to human health and the environment. It is the catalytic converter’s job to lessen these pollutants by converting them into less harmful substances, namely carbon dioxide, nitrogen, and water vapor.
The working of a catalytic converter revolves around a complex chemical process. The harmful gasses from the engine flow into the converter, where they encounter a densely honeycombed ceramic structure coated with catalysts. These catalysts trigger chemical reactions that transform the toxic substances.
The first stage of this process takes place in the reduction catalyst, where platinum and rhodium help convert nitrogen oxides into nitrogen and oxygen. Following this, the gasses enter the oxidation catalyst. Here, platinum and palladium facilitate the conversion of carbon monoxide into carbon dioxide and hydrocarbons into water and carbon dioxide. In essence, the converter takes harmful exhaust gasses and ‘cleans’ them before they exit the truck’s tailpipe.
The Strategic Positioning of the Catalytic Converter
The converter’s location within the exhaust system is critical for it to function effectively and contribute to a truck’s overall performance.
Location of a Semi Truck’s Catalytic Converter
In a semi truck, the catalytic converter is typically found within the exhaust system, between the engine and the muffler. It’s often located underneath the vehicle to keep it out of the way and protect it from potential damage.
The exhaust gasses generated by the engine must pass through the catalytic converter before they’re expelled out of the exhaust pipe. Therefore, having the converter positioned closer to the engine allows it to receive the exhaust gasses at higher temperatures, which is beneficial as the chemical reactions inside the converter require high heat to be effective.
Why is the Catalytic Converter Located There?
The placement of the catalytic converter has been carefully considered to ensure optimal function, efficiency, and safety.
- Function and Efficiency: Catalytic converters need to be exposed to high temperatures to effectively facilitate the necessary chemical reactions. Placing the converter closer to the engine, where the exhaust gasses are hottest, allows it to work more efficiently.
- Safety: The catalytic converter can get extremely hot during operation. Placing it underneath the truck, away from the vehicle’s interior and other sensitive parts, minimizes the risk of heat-related damage or accidents.
- Convenience and Protection: The underbody location provides a certain level of protection to the converter against potential impacts or damages. It’s also conveniently placed for mechanics to access during maintenance or repairs.
Implications of the Catalytic Converter’s Location
The catalytic converter’s strategic positioning in a semi truck has significant implications. It influences its performance, safety, maintenance, and even the laws and regulations related to emission standards.
How the Catalytic Converter’s Positioning Affects Its Function
The catalytic converter’s location near the engine, where the exhaust gasses are hottest, allows it to function more efficiently. The high temperatures facilitate the chemical reactions within the converter, enabling it to effectively reduce harmful emissions.
The underbody location also provides an uninterrupted flow path for the exhaust gasses. This position allows for the seamless transition of gasses from the engine through the converter, and out the exhaust pipe. Any hindrance in this path can negatively impact the engine performance.
Impact of the Converter’s Location on Semi Truck Performance
The converter’s location can also influence the overall performance of the semi truck. For instance, if the converter is clogged or damaged, it can obstruct the exhaust gas flow, leading to engine problems. Symptoms could include reduced power, lower fuel efficiency, and rough idling.
Furthermore, due to the high operating temperatures, a malfunctioning converter can cause overheating issues, potentially damaging nearby components or leading to a fire risk. Thus, regular inspections and maintenance of the catalytic converter are vital to ensure optimal truck performance and safety.
Location Influence on Catalytic Converter Maintenance and Repair
The converter’s underbody placement has both advantages and disadvantages when it comes to maintenance and repair. On the one hand, its location protects it from most road impacts, minimizing the risk of physical damage.
On the other hand, its positioning exposes it to potential corrosion from road salts or water, which can lead to damage over time. Also, it can be vulnerable to theft due to the precious metals it contains. Therefore, periodic underbody inspections are recommended to check for any signs of corrosion, damage, or tampering.
In addition, its location can make certain repairs more labor-intensive, possibly requiring the vehicle to be lifted for better access. However, this placement is typically more convenient for professional mechanics equipped with the necessary tools and lifting equipment.
Catalytic Converter Laws and Regulations
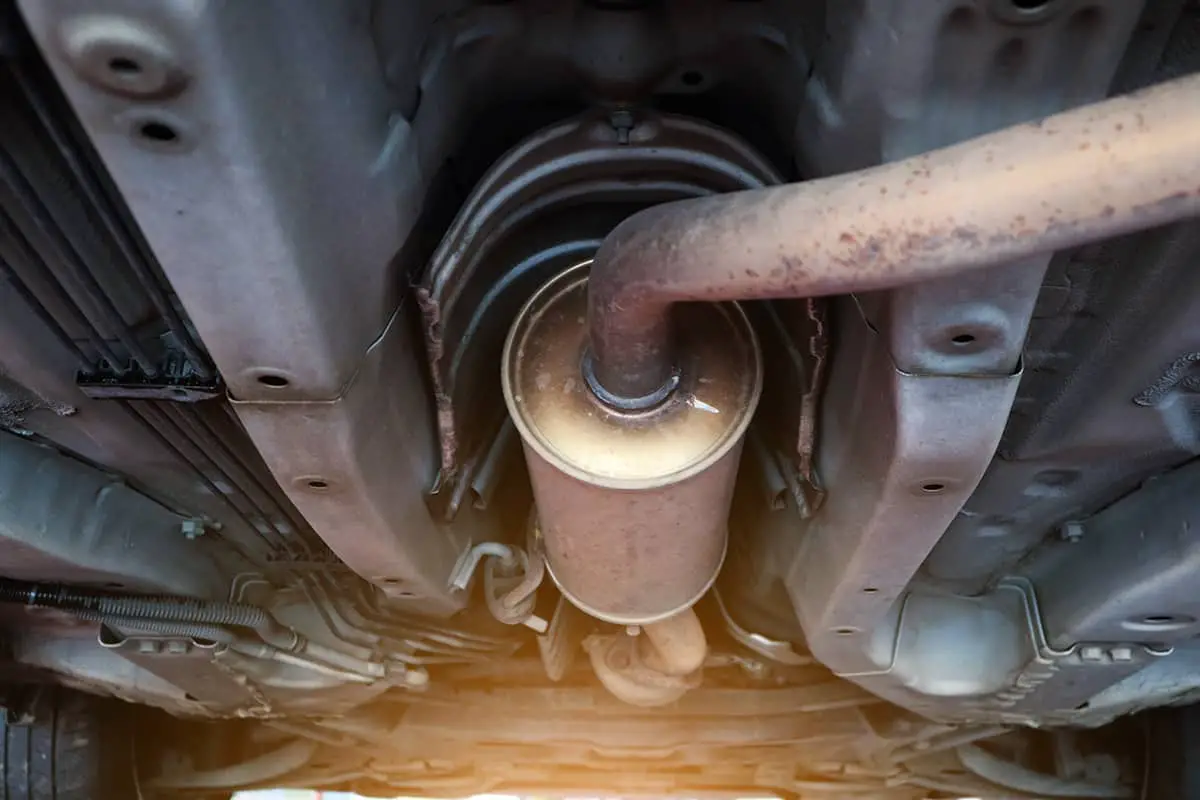

Catalytic converters are subject to various laws and regulations due to their critical role in emission control. These rules are designed to protect the environment by ensuring that vehicles, including semi trucks, limit their emission of harmful gasses.
Emission Standards for Semi Trucks
Semi trucks, like all motor vehicles, must adhere to emission standards established by environmental agencies. In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) sets these standards, which limit the amount of pollutants that a truck can emit. Catalytic converters play a crucial role in helping trucks meet these standards by reducing the harmful emissions from the exhaust.
Most modern semi trucks are equipped with advanced catalytic converter systems, such as Diesel Oxidation Catalysts (DOC) or Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) systems, to effectively control the emission of pollutants and comply with these strict standards.
Regulations Concerning Catalytic Converter Replacement
Catalytic converters can wear out or become damaged, requiring replacement. However, replacing a catalytic converter isn’t as simple as swapping it out. There are regulations in place to ensure that the replacement converter is compliant with the necessary standards.
In general, replacement converters must be approved by the EPA or the relevant environmental authority in your jurisdiction. Using non-approved converters or removing the converter altogether is against the law and can result in substantial fines.
Laws on Catalytic Converter Theft
Due to the precious metals they contain, catalytic converters are often a target for thieves. To combat this, many jurisdictions have laws and regulations in place regarding the buying and selling of used catalytic converters.
For instance, many states require documentation (PDF) proving ownership of the converter before it can be sold. Scrap metal dealers are often required to maintain records of catalytic converter transactions, including the seller’s information, to discourage theft and illegal sales.
Legal Consequences of Non-Compliance
Failure to comply with catalytic converter laws and regulations can result in substantial penalties, including fines and even imprisonment in some cases. Non-compliant vehicles can also be barred from operation, negatively impacting business operations for commercial truck owners.