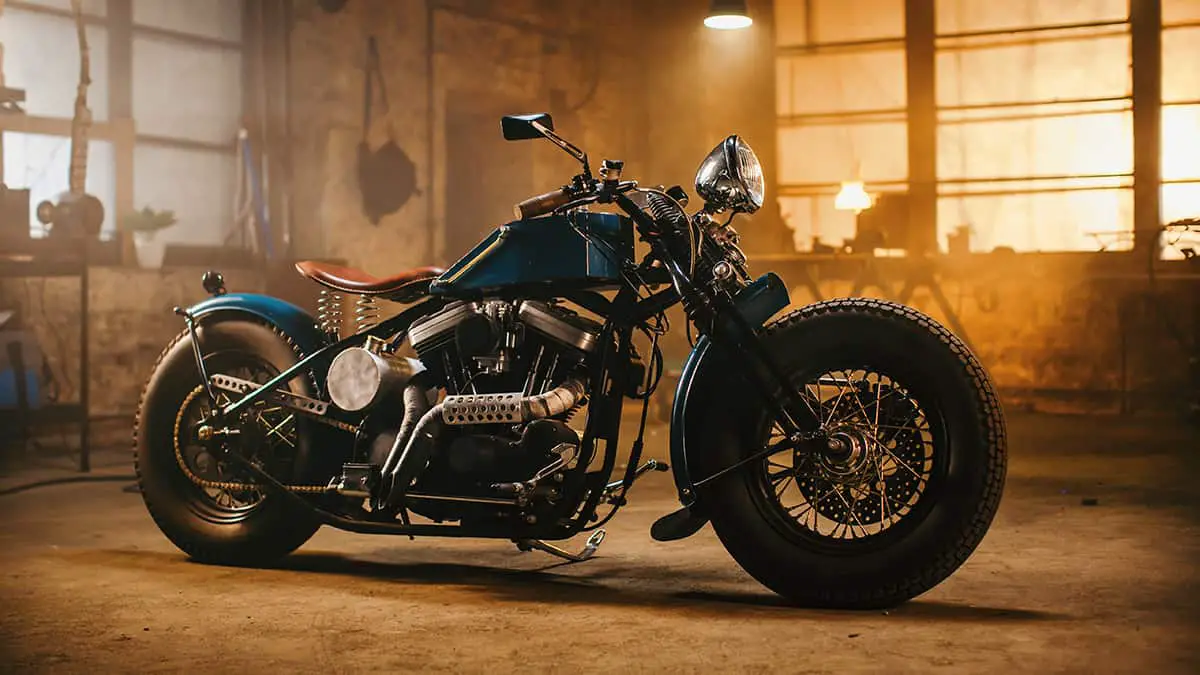
Riding a motorcycle can be an exhilarating experience, but have you ever stopped to wonder about the intricate parts that make up this two-wheeled machine? From the engine to the wheels, each component plays a crucial role in ensuring a smooth and safe ride.
The anatomy of a motorcycle consists of but is not limited to the following parts:
- Frame
- Engine
- Transmission system
- Suspension
- Braking system
- Wheels and tires
- Fuel system
- Exhaust system
- Electrical system
- Controls and accessories
Here, we’ll explore the various components and subcomponents that make up a hog. I’ll also include a few maintenance tips for some of the more important motorcycle parts. You may find this diagram below handy when referring to the detailed parts of a motorbike.
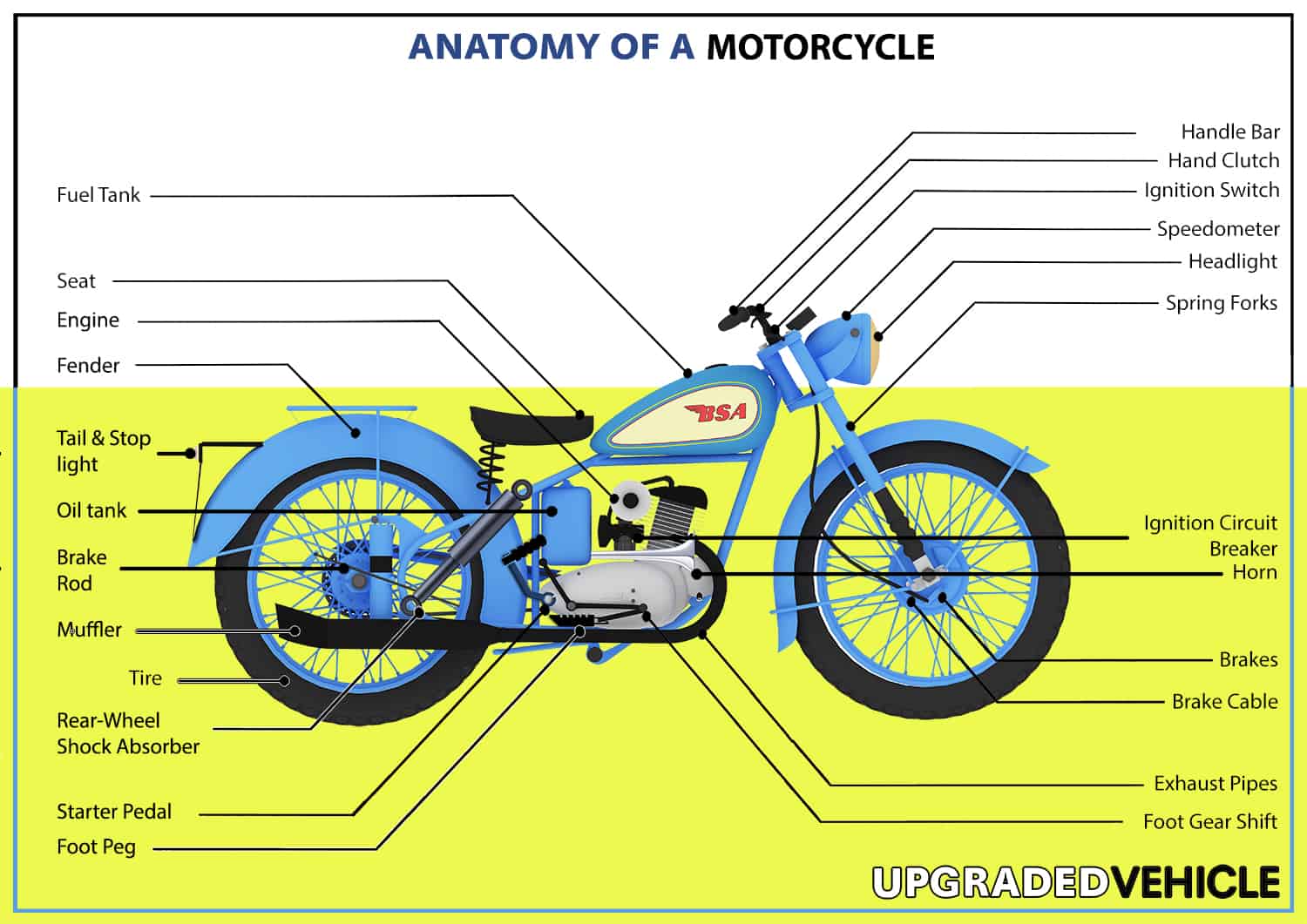
Parts of a Motorcycle
A motorcycle is made up of a multitude of parts, each playing a vital role in its overall function. Understanding these elements can help riders troubleshoot problems and maintain their bikes in top condition.
It would take quite some time to list every single component, but we will highlight the most important parts and subcomponents. So, let’s take a closer look at the essential parts that make up a motorcycle, from the engine to the brakes and everything in between.
1. Frame
The motorcycle frame serves as the bike’s backbone, providing support and stability for all other components. It plays a crucial role in determining handling, overall performance, and rider safety. There are various frame designs, such as cradle, perimeter, and trellis. The frame consists of the main structure, steering head, swingarm pivot, and mounting points for the engine, suspension, and other components.
Regularly inspect the frame for signs of damage, corrosion, or cracks. Repair or replace any damaged sections promptly to ensure safety and structural integrity.
2. Engine
The engine is the heart of a motorcycle, responsible for converting fuel into mechanical energy to drive the bike. Engines come in various configurations, sizes, and power outputs, affecting performance and riding characteristics.
Motorcycle engines come in different types, including single-cylinder, parallel-twin, V-twin, and inline-four. These engines have key components such as cylinders, pistons, and valves.
Perform regular oil changes, replace air filters, and check valve clearances to ensure optimal engine performance and longevity.
3. Transmission system
The transmission system transfers power from the engine to the rear wheel, allowing the motorcycle to change speeds and maintain efficient performance across different riding conditions. Key components include the gearbox, clutch, and drive systems (chain, belt, or shaft).
Lubricate the chain or belt, adjust the clutch cable, and inspect the gearbox for wear or damage to maintain smooth and efficient operation.
4. Suspension
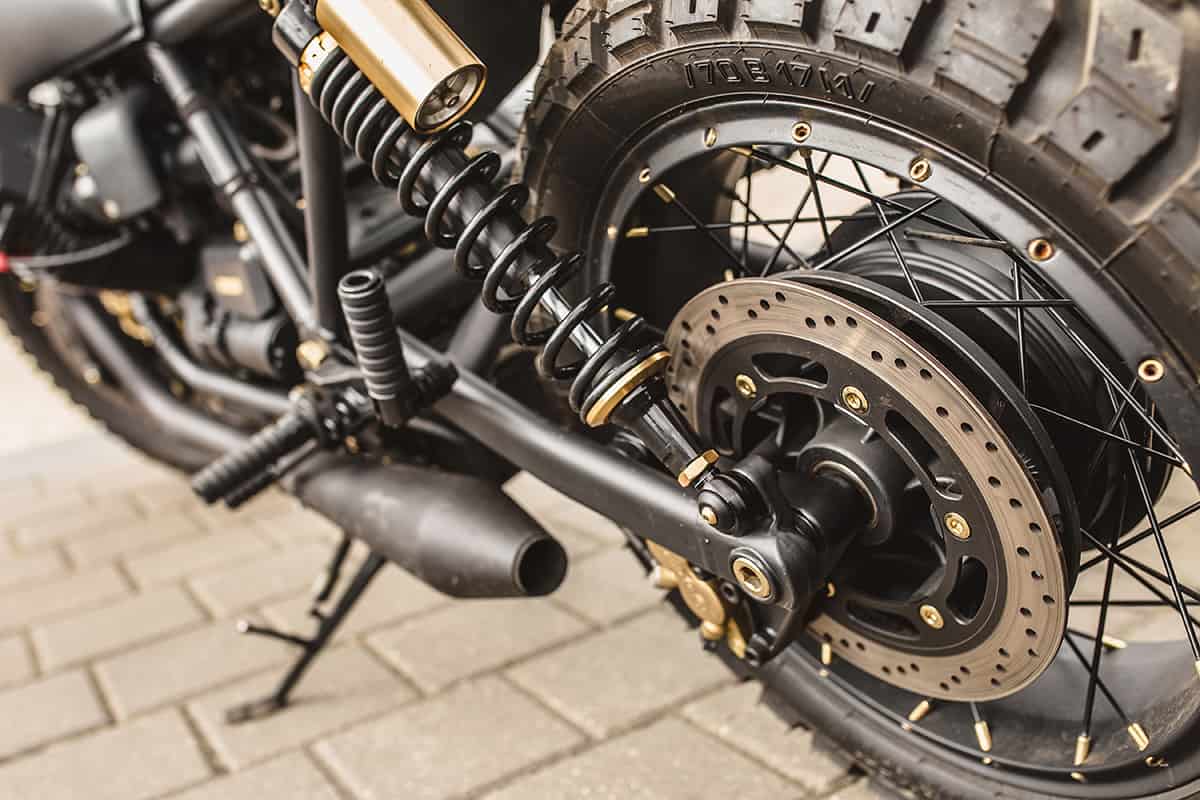

The suspension system provides stability and absorbs road irregularities, contributing to a comfortable and controlled ride. It affects handling, braking, and overall performance. Front suspension types include telescopic forks and upside-down forks, while rear suspension options are twin shock and monoshock.
Inspect suspension components for wear or damage, replace worn parts, and adjust settings for optimal performance and rider comfort.
5. Braking system
Motorcycle brakes are either disc or drum brakes. Disc brakes are more common and consist of brake pads and rotors. Regular brake maintenance includes inspecting the brake pads, rotors, and fluid levels. Replace worn pads and bleed the brake system as needed.
Regularly inspect brake pads, rotors, and fluid levels. Replace worn pads, bleed the brake system, and repair any leaks or damage to maintain optimal braking performance.
6. Wheels and tires
Wheels and tires connect the motorcycle to the road, influencing handling, traction, and ride comfort. They come in various materials and designs to suit different riding styles and conditions. Motorcycles use various wheel types, such as spoked or cast alloy wheels. Wheels consist of the wheel hub, rim, and spokes or cast structure. Tires have tread patterns, sidewalls, and beads.
Check tire pressure and tread depth regularly. Inspect wheels for damage, and replace worn or damaged tires to ensure safe and efficient riding.
7. Fuel system
The fuel system delivers fuel from the tank to the engine, ensuring efficient combustion and power generation. Fuel systems may utilize carburetors or fuel injection technology. The fuel system consists of the fuel tank, carburetor or fuel injection system, and fuel lines.
Keep the fuel tank clean, check for leaks in the system, and replace the fuel filter regularly to maintain efficient fuel delivery and performance.
8. Exhaust system
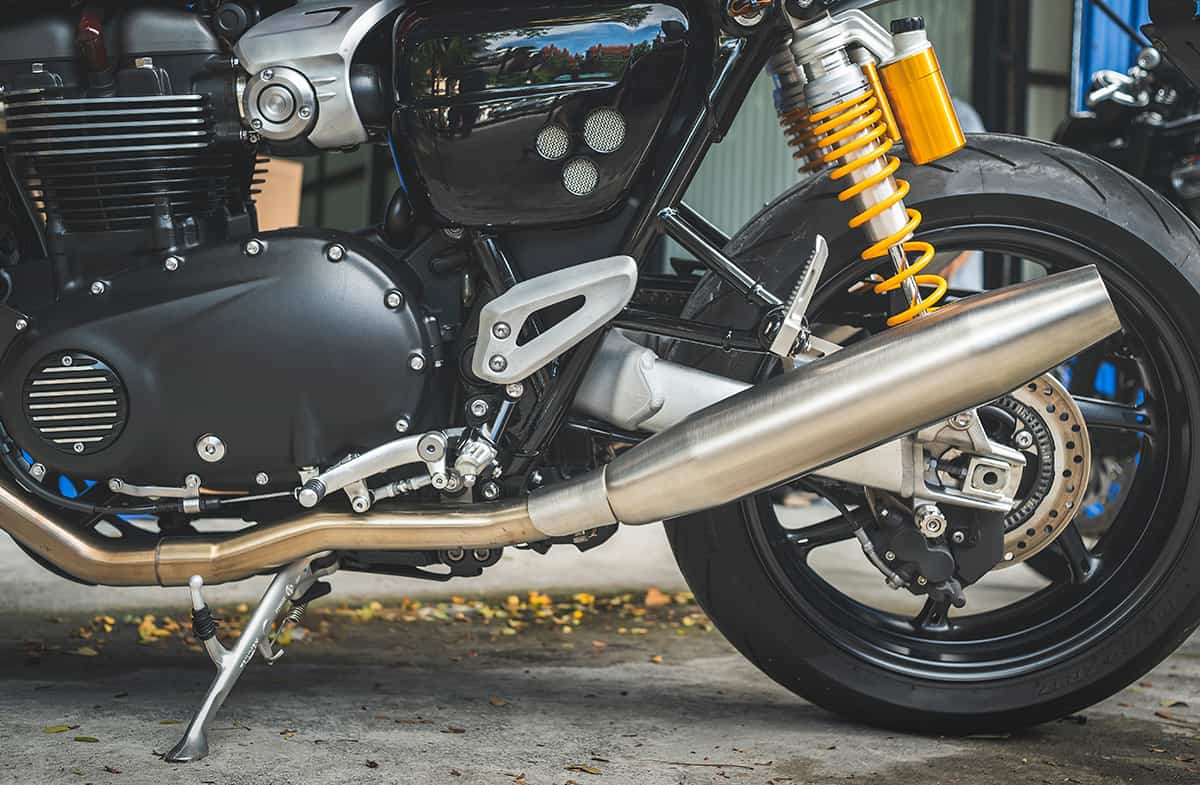

The exhaust system expels burned gases from the engine, reducing noise and emissions while enhancing performance. Exhaust systems vary in design and performance characteristics.
Common types include single, dual, and aftermarket performance exhausts. Exhaust systems consist of headers, mid-pipes, mufflers, and exhaust tips, with the Subcomponents of the exhaust system including the exhaust manifold, catalytic converter (if applicable), pipes, and muffler.
Regularly inspect the system for leaks, corrosion, and loose fittings. Address any issues promptly to maintain optimal performance and avoid further damage.
9. Electrical system
The electrical system powers various components on a motorcycle, including the battery, charging system, lighting, and instrument panel. It is essential for starting the engine, illuminating the road, and providing vital information to the rider. The electrical system powers components like the battery, charging system, lighting, and instrument panel.
Keep the battery charged, inspect the wiring for damage or wear, and replace burned-out bulbs to ensure the system functions correctly and safely.
10. Controls and accessories
Controls and accessories on a motorcycle include handlebars, hand controls (brakes, clutch, and throttle), foot controls (gear shifter and rear brake), and custom accessories.
These parts allow riders to operate the motorcycle and personalize it to suit their preferences and needs. Custom accessories and aftermarket parts allow you to personalize your bike. Inspect controls for wear and adjust them for comfort and proper functioning.
Regularly inspect controls for wear or damage, lubricate moving parts, and adjust them for comfort and proper functioning. Consider upgrading or customizing controls and accessories to improve comfort, safety, or aesthetics.
Additional Motorcycle Parts
The following parts do not play a direct role in a motorcycle’s performance (except perhaps with aerodynamics).
1. Body panels
Body panels on a motorcycle include fairings, side panels, and fenders. They provide aerodynamic benefits, protect the engine and other components from debris, and contribute to the bike’s overall aesthetics. Subcomponents of body panels can include upper and lower fairings, side panels, radiator covers, and fenders.
2. Foot pegs
Foot pegs are the supports on a motorcycle where the rider rests their feet. They play a crucial role in the rider’s comfort and control of the bike, providing a stable platform for shifting gears and applying the rear brake. Subcomponents of foot pegs can include the peg itself, mounting brackets, and rubber or metal grips.
3. Swingarm
The swingarm is the rear suspension component that connects the motorcycle frame to the rear wheel. It pivots on the frame, allowing the rear wheel to move up and down in response to bumps and changing road conditions. Subcomponents of the swingarm include the swingarm itself, the pivot bolt, and the rear axle.
4. Mudguards
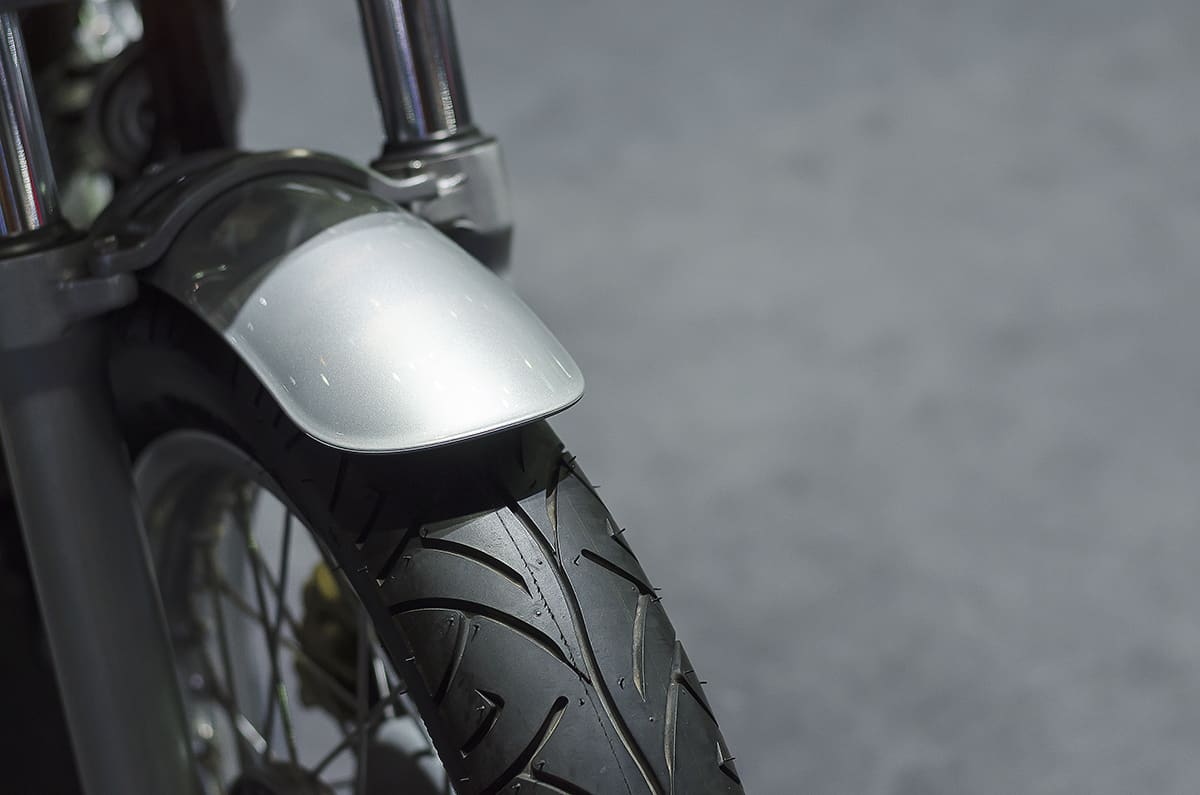

Mudguards, also known as fenders, are protective covers that shield the motorcycle and rider from water, mud, and debris. They are typically mounted above the front and rear wheels, preventing dirt and water from being flung into the air. Subcomponents of mudguards can include the mudguard itself and mounting brackets or hardware.
5. Mirrors
Mirrors are essential safety components on a motorcycle, providing the rider with a clear view of the road behind. They are typically mounted on the handlebars or fairings, depending on the motorcycle’s design. Subcomponents of mirrors include mirror glass, mirror housing, and mounting hardware.
6. Seat
The seat provides comfort and support for the rider and, in some cases, a passenger. Motorcycle seats come in various shapes, sizes, and materials, with some offering additional features like storage compartments or adjustable positioning. Subcomponents of the seat can include the seat base, foam padding, seat cover, and mounting hardware.
FAQs
1. What are the most critical motorcycle parts to maintain?
The most critical motorcycle parts to maintain are the engine, brakes, tires, and suspension. Regular oil changes, air filter replacements, and valve clearance checks ensure optimal engine performance.
Inspect and maintain brake components, including pads, rotors, and fluid levels. Monitor tire pressure, and tread depth, and replace worn tires. Lastly, adjust and maintain the suspension system for better handling and ride quality.
2. How can I customize my motorcycle for a better riding experience?
To customize your motorcycle for a better riding experience, consider upgrading the suspension, exhaust, and tires for improved performance. Adjust the ergonomics with custom handlebars, foot pegs, or seats for greater comfort. Add accessories like windshields, luggage racks, or advanced lighting for increased functionality and personal style.
3. What are the signs of a failing motorcycle part?
Signs of a failing motorcycle part include unusual noises, vibrations, or performance issues. Leaks, visible damage, or excessive wear can also indicate a problem. Pay attention to any changes in handling, acceleration, or braking, as these may signal a failing component.
4. What should I do if I encounter a problem with one of my motorcycle’s parts?
If you encounter a problem with one of your motorcycle’s parts, consult the owner’s manual for guidance on diagnosis and repair. If you’re unable to address the issue yourself, consult a professional mechanic for assistance. Regular maintenance and prompt attention to any issues will ensure your motorcycle remains safe and reliable.






