The O2 sensor, or oxygen sensor, monitors the levels of unburned oxygen in your vehicle’s exhaust system. It acts as a vigilant watchdog, ensuring that your engine is running at optimal efficiency and helping to maintain your vehicle’s emission standards.
When it works as intended, it keeps your car performing smoothly. However, in some circumstances, it may be necessary or advantageous to bypass this sensor.
To bypass an O2 sensor, you must:
- Identify the O2 sensor in your car.
- Disconnect it from the exhaust system.
- Attach a resistor or simulator to fool the car’s computer into thinking the sensor is still functioning.
This guide aims to will cover the workings of the O2 sensor, the reasons for bypassing it, and the step-by-step process involved.
How an O2 Sensor Works
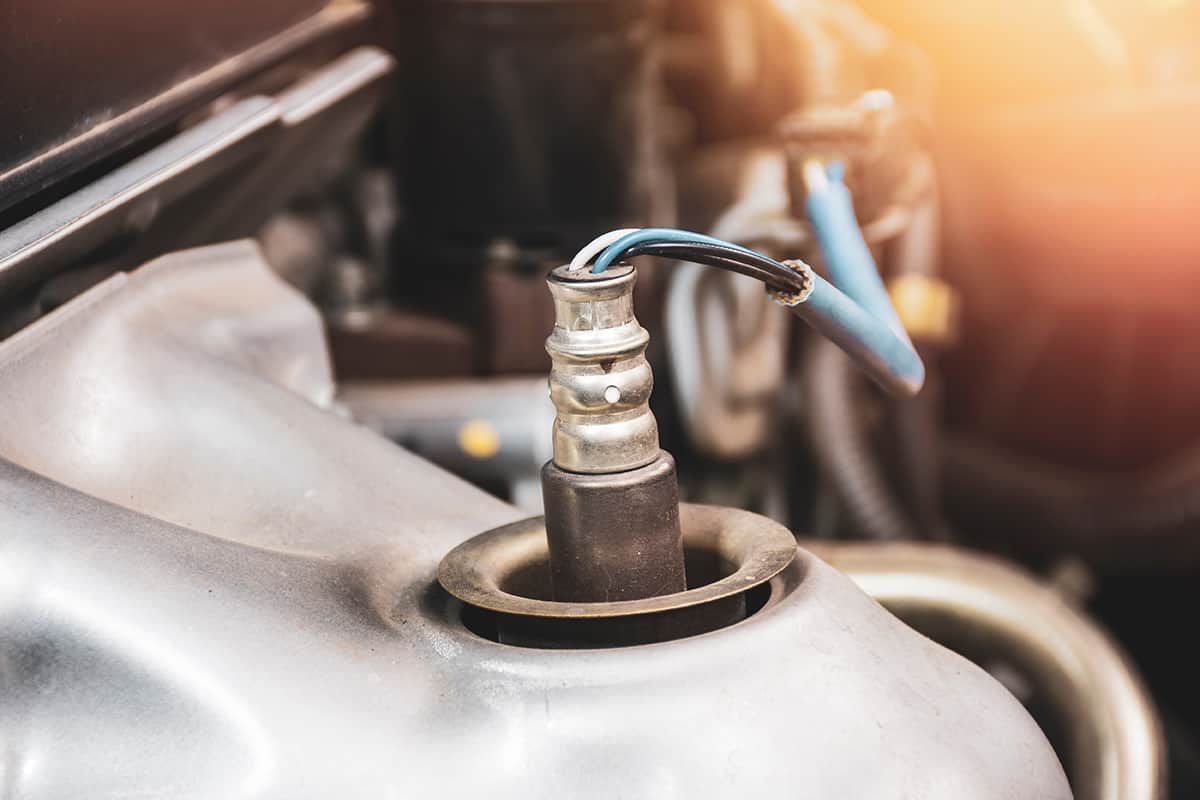

The oxygen sensor, commonly referred to as an O2 sensor, is a crucial part of your car’s exhaust system. Its primary role is to monitor the amount of oxygen present in the exhaust gasses leaving your engine.
Composition and Design of an O2 Sensor
The O2 sensor is a small device, often not much larger than a spark plug, made up of ceramic coated with layers of platinum and other metals. This sensor is typically located in the exhaust manifold, downstream from the engine, though some cars have multiple sensors placed at different points in the exhaust system.
Each sensor features a tip that protrudes into the exhaust flow. The sensor’s casing houses a chemical reaction chamber that interacts with the exhaust gasses. The sensor generates a voltage based on the difference in oxygen concentration between the exhaust gas and the outside air.
How the O2 Sensor Influences Emissions
Beyond performance and fuel efficiency, the O2 sensor significantly impacts your car’s emissions. A well-functioning O2 sensor ensures the optimal burning of fuel, which reduces the release of harmful pollutants into the atmosphere.
If the air-fuel mixture is too rich, there’s insufficient oxygen for complete combustion, resulting in unburnt fuel (hydrocarbons) being expelled through the exhaust.
Conversely, if the mixture is too lean, combustion temperatures rise, leading to increased nitrogen oxide emissions. Both scenarios are harmful to the environment, making the O2 sensor a key component in reducing a vehicle’s environmental impact.
Common Reasons for Bypassing the O2 Sensor
Despite the vital role the O2 sensor plays in maintaining engine efficiency and controlling emissions, there are instances where individuals might bypass it. Here we’ll delve into the common reasons why this action is undertaken.
Dealing with O2 Sensor Failure
An O2 sensor can last for about 100,000 to 150,000 miles under normal conditions, but various factors can lead to its premature failure. When the O2 sensor fails, it can provide inaccurate information to the engine control unit (ECU), leading to poor engine performance, reduced fuel efficiency, and increased emissions.
Bypassing the faulty O2 sensor can be a temporary solution to these problems until the sensor is replaced. Bypassing the O2 sensor should not be considered a permanent solution, as the sensor plays a vital role in ensuring the proper functioning of your vehicle.
Temporary Fixes and Diagnostic Purposes
Another reason for bypassing the O2 sensor is for diagnostic purposes. Suppose your vehicle is experiencing performance issues, and you suspect the O2 sensor might be the culprit. In that case, you could bypass the sensor temporarily to see if the performance issues persist. If the problems cease, it’s a strong indication that the O2 sensor was indeed the problem.
In situations where immediate repair isn’t possible or affordable, a temporary bypass can keep a vehicle running. But again, this is a stopgap measure and not recommended as a long-term solution.
Steps to Bypass the O2 Sensor
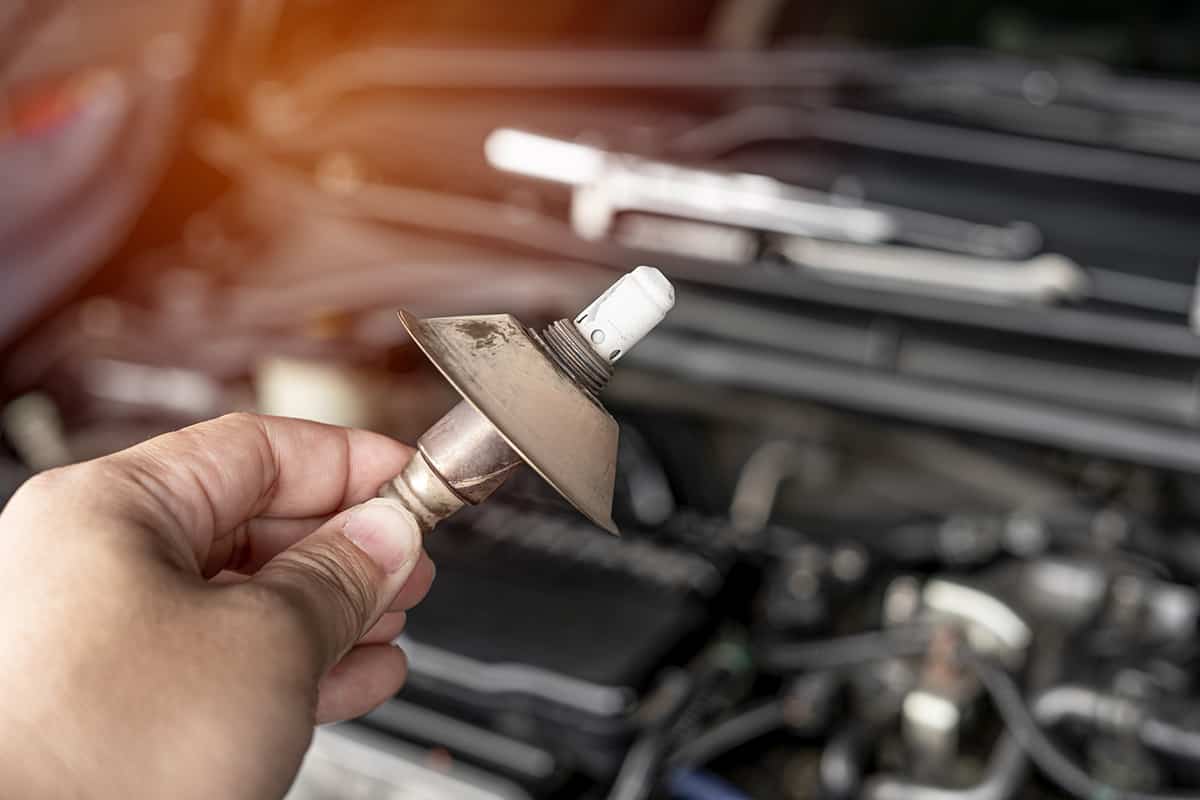

Bypassing an O2 sensor can be valuable for diagnostic purposes or in case of an emergency. This section will guide you through the steps involved in bypassing the O2 sensor.
Before starting, ensure you have the necessary tools: a wrench or socket set suitable for the O2 sensor, electrical tape, a 1 Megaohm resistor, and insulated connectors. Also, make sure your vehicle has cooled down to avoid burns from the exhaust system.
Always disconnect the battery before working on any electrical component of the vehicle. Furthermore, make sure the vehicle is properly supported if you need to get underneath it.
1. Locating the O2 Sensor
The O2 sensor is typically located on the exhaust pipe, either before (upstream) or after (downstream) the catalytic converter. Some vehicles have multiple O2 sensors, so be sure you’re working with the correct one. Your vehicle’s service manual can provide specifics about the location of the O2 sensor.
2. Disconnecting the O2 Sensor
Once the O2 sensor has been located, use the wrench or socket to disconnect it from the exhaust pipe. Be careful not to damage the wiring or the sensor itself if you plan to reuse it.
3. Wiring the Resistor
To bypass the O2 sensor, a resistor can be used to mimic the sensor’s normal output. Connect the 1 Megaohm resistor to the positive wire that was connected to the O2 sensor. Secure the connection with an insulated connector and seal it with electrical tape to prevent shorts.
4. Reconnect and Test
Reconnect the battery and start the vehicle. Check for any error codes on the dashboard. If the process was successful, the error code for the O2 sensor should no longer be present.
Alternatives to Bypassing the O2 Sensor
While bypassing the O2 sensor might appear as a quick fix, it’s not the most responsible or sustainable solution. This section aims to discuss viable alternatives to bypassing the O2 sensor to maintain your vehicle’s health and performance.
Regular Maintenance and Inspection
As with all components of a vehicle, regular maintenance is key to avoiding problems with the O2 sensor. Adhering to the manufacturer’s recommended service intervals ensures the vehicle’s sensors, including the O2 sensor, are inspected and maintained regularly.
Regular maintenance and inspections can identify if an O2 sensor is dirty or wearing out and needs replacement. This prevents sensor failure, ensuring the vehicle’s fuel efficiency and performance aren’t affected.
Replacing the O2 Sensor
If the O2 sensor is malfunctioning or faulty, the best course of action is usually to replace it. The cost of an O2 sensor replacement can vary, but it’s generally a cost-effective solution considering the potential impact on the vehicle’s performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions.
Replacing an O2 sensor involves locating the sensor (usually on the exhaust pipe), disconnecting it from the wiring harness, unscrewing it from the exhaust pipe, and installing the new one in its place. Always consult your vehicle’s service manual or a professional mechanic for specific instructions for your vehicle model.
Using Fuel Additives
Certain fuel additives are designed to clean the fuel system, including the components that can affect the O2 sensor. These additives can remove carbon deposits, improving the engine’s overall efficiency and potentially prolonging the life of the O2 sensor.
There are many fuel additives on the market, so it’s crucial to choose one that’s suitable for your vehicle and its fuel type. Always follow the instructions provided on the product’s packaging.
Professional Diagnostics and Repair
When dealing with O2 sensor issues, one of the best alternatives to bypassing the sensor is seeking professional help. Automotive technicians have specialized tools to diagnose and repair O2 sensor problems accurately. This can prevent unnecessary replacements and ensure the issue is addressed correctly.