Turbochargers have long been celebrated in the automotive world for their remarkable ability to significantly boost a car’s horsepower. These ingenious devices harness the power of exhaust gases, compressing and redirecting air into the engine to create a more potent combustion process. This, in turn, improves the engine’s efficiency and power output.
On average, a turbocharger can add 10-50% more horsepower to your car or between 40 and 300 HP. The actual gain varies based on factors like engine size, turbo type, and setup. Given these impressive power boosts, adding a turbocharger can be a highly worthwhile upgrade, as long as the installation is done correctly and the engine is well-maintained.
In this guide, we’ll cover the specifics of turbochargers, how they impact horsepower, what factors influence this power increase, and the various types of turbochargers.
Basics of Turbochargers
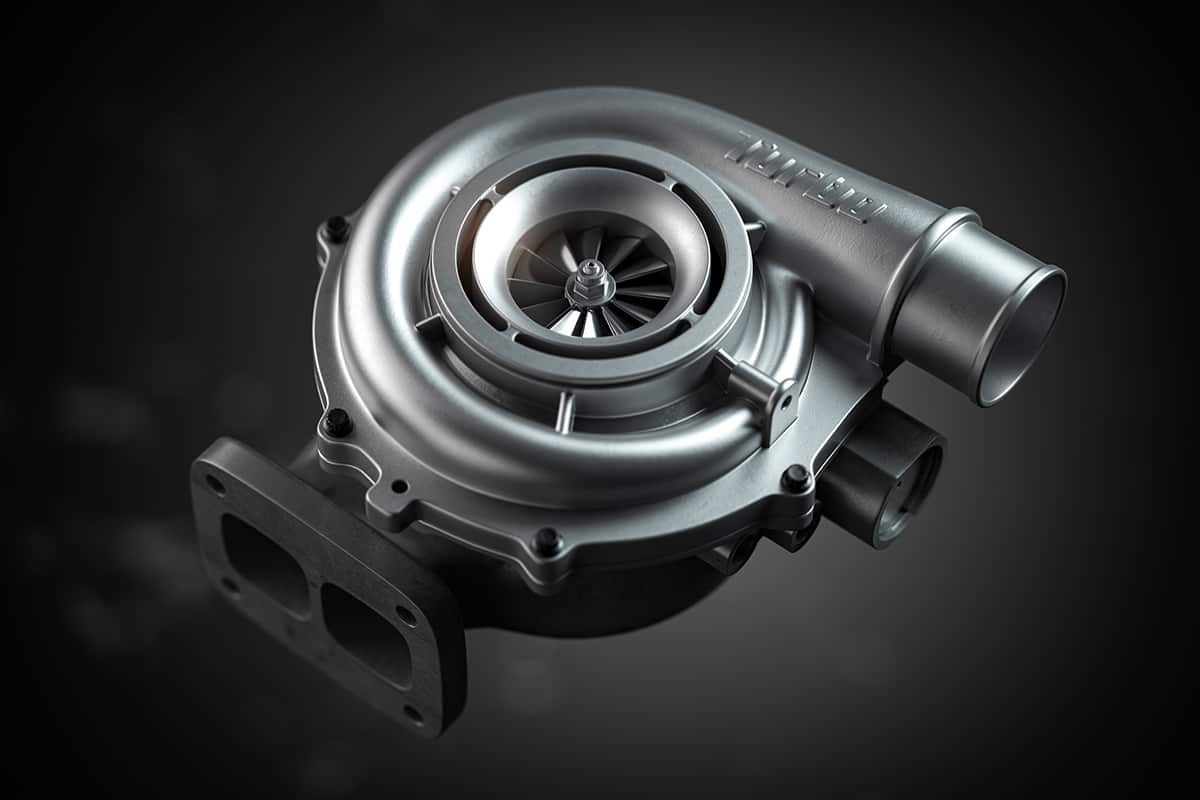

A turbocharger is essentially a forced induction system. It pushes more air into the engine’s combustion chamber, allowing it to burn more fuel and do more work, thus enhancing its horsepower. It accomplishes this using the energy from the exhaust gases that would otherwise be wasted.
The turbocharger consists of two main components connected by a shaft: the turbine and the compressor.
The turbine resides in the exhaust stream from the cylinders. The energy from the hot, fast-moving exhaust gases spins the turbine, which turns the connected shaft.
As the shaft spins, the compressor, which draws in and compresses ambient air, also spins. The compressed air gets forced into the engine, leading to a more powerful combustion.
Let’s break down the parts of a turbocharger further:
- Turbine Housing and Wheel: This component takes exhaust gases from the engine and uses their energy to spin the turbine wheel. The design of the housing focuses the energy onto the turbine for maximum efficiency.
- Compressor Housing and Wheel: The spinning turbine also spins the compressor wheel. The compressor wheel draws in and compresses air before sending it to the engine. The housing’s design increases pressure and directs air towards the engine.
- Center Housing: This is essentially the “control center” of the turbocharger, housing the bearings that support the shaft connecting the turbine and compressor, and the oiling system that lubricates them.
- Wastegate: This is a valve that diverts excess exhaust gas away from the turbine wheel when the turbocharger is producing the desired boost level. It helps control the speed of the turbocharger.
- Intercooler: While not part of the turbocharger itself, this component is often associated with them. As air is compressed, it heats up, and hot air is less dense. An intercooler cools the compressed air, making it denser for a more powerful combustion.
The Correlation between Turbochargers and Horsepower
As we’ve explored, turbochargers enhance engine power by forcing more air into the combustion chamber. But how does this correlate to horsepower?
Fundamentals of Horsepower
Horsepower is a measure of work done over time. In the automotive context, it’s a measure of an engine’s output—the higher the horsepower, the more powerful the engine. It’s all about how much fuel and air mixture an engine can burn and how efficiently it can convert this combustion into motion. More air and fuel equal more combustion, which equals more power.
How Turbochargers Affect Engine Performance
This is where the turbocharger steps in. By forcing more air into the engine, turbochargers allow for more fuel to be burnt in the combustion process, thus generating more power. A turbocharger doesn’t just provide extra power on demand but also enhances the engine’s overall efficiency.
At lower engine speeds, the turbo isn’t doing much. But as the engine speed and exhaust gas volume increase, the turbo begins to force more air into the engine. This equates to a noticeable boost in performance at higher engine speeds.
Turbochargers and Horsepower
Turbochargers are designed to enhance an engine’s horsepower by making use of otherwise wasted exhaust gases.
Horsepower is directly proportional to the air/fuel mixture that an engine can combust. By compressing and pushing more air into the engine, turbochargers allow for a higher air/fuel mixture volume.
However, it’s not just about the peak horsepower that a turbocharger can add. Turbochargers can also widen an engine’s powerband—the range of engine speeds at which it can operate most efficiently. This means you’re not just getting more power, but more usable power across a wider range of engine speeds.
How Much Horsepower Does a Turbocharger Add?
If you’ve come this far, you’re undoubtedly aware that a turbocharger can considerably increase your vehicle’s horsepower. However, the question remains: exactly how much horsepower can a turbocharger add?
Factors that Determine the Increase in Horsepower
The horsepower gain from a turbocharger isn’t a constant figure. It relies on several factors, each playing a significant role in the final output.
- Engine Specifications: Your engine’s size, design, and existing performance will heavily influence the horsepower gains from a turbocharger. A larger, more powerful engine will generally gain more horsepower from a turbocharger than a smaller, less powerful one.
- Turbocharger Size: The size of the turbocharger you install will also influence the horsepower gains. Larger turbochargers can generate more boost and, thus, more horsepower but may suffer from increased turbo lag. Smaller turbochargers may provide less peak power but deliver a smoother power curve with less lag.
- Fuel Quality and Delivery: Your engine needs to match the increased air from the turbocharger with increased fuel for combustion. The quality of the fuel and the efficiency of the fuel delivery system can both affect the horsepower gain.
- Engine Tuning: Once a turbocharger is installed, the engine will often need to be tuned to handle the increased air and fuel mixture. An effective tune can maximize the horsepower gains from a turbocharger.
Estimating Potential Horsepower Gains from Turbocharging
Given the right conditions and a well-matched turbocharger, you can expect a 10% to 50% horsepower increase. However, this is a rough estimate, and actual gains can be higher or lower depending on the factors above.
For example, if you add a turbocharger to a stock four-cylinder engine with 150 horsepower, you could increase its output to between 165 and 225 horsepower. This additional power would provide a noticeable improvement in acceleration and overall performance.
Types of Turbochargers and Their Impact on Horsepower
There is a variety of turbocharger types, each with their unique design features, strengths, and weaknesses.
Single Turbo

A single turbo setup uses one turbocharger. It can provide a significant power boost and is simpler and cheaper to install than more complex setups.
Twin-Turbo
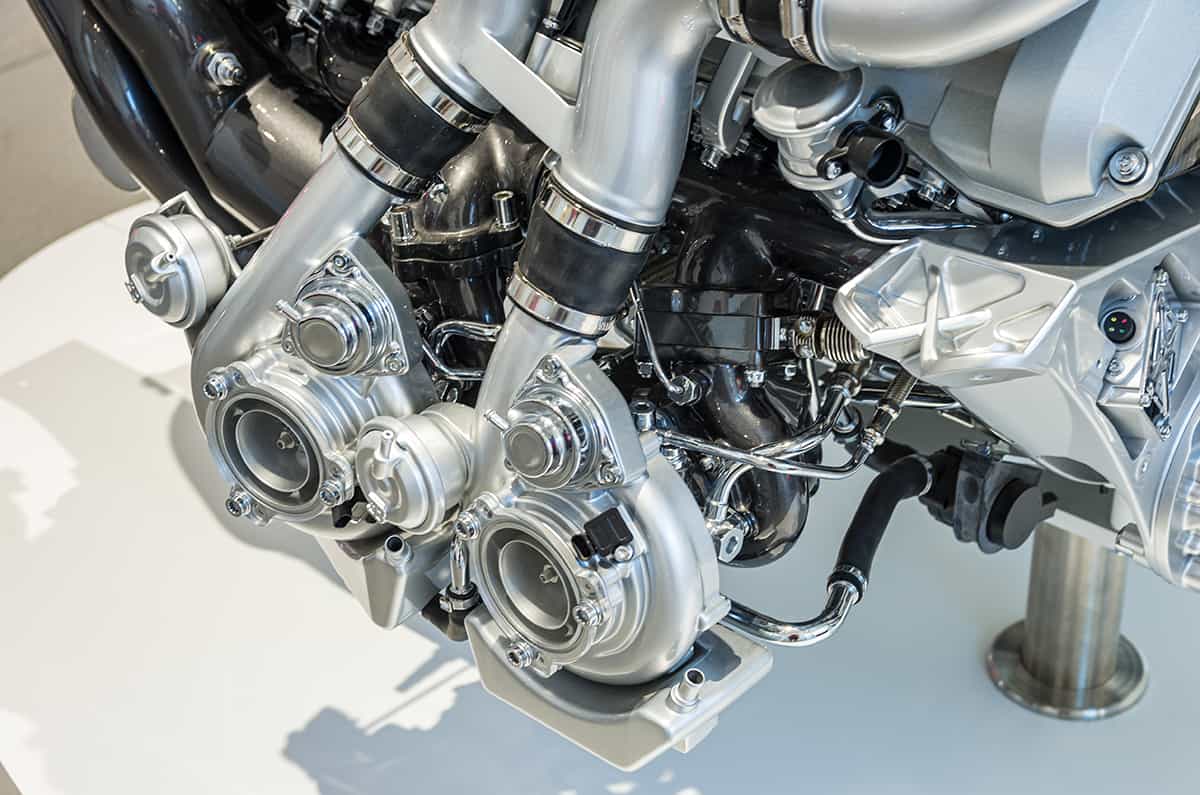
Twin-turbo setups use two turbochargers. They can be set up in two ways: parallel or sequential. Parallel twin turbos distribute the exhaust gases equally between two turbos. This setup can provide more power than a single turbo and can reduce turbo lag. Sequential twin-turbos use one small and one large turbo.
Variable Geometry Turbocharger
Variable geometry turbochargers use vanes in the turbine housing that can change position to control the flow of exhaust gases onto the turbine. This allows the turbo to act like a small turbo at low engine speeds and a large turbo at high speeds, providing the benefits of both.
Twin-Scroll Turbocharger
Twin-scroll turbochargers use two separate chambers in the turbine housing. This design allows the turbo to harness exhaust gases more efficiently, reducing turbo lag and improving throttle response. Twin-scroll turbos can provide better performance throughout the rev range than a single-scroll turbo.
Electric Turbocharger
Electric turbochargers use an electric motor to spin the compressor before the exhaust gases take over. This can eliminate turbo lag and provide instant power from a stop, improving the driving experience at low speeds.