As a component responsible for transmitting power from the engine to the wheels, the transmission plays a critical role in your vehicle’s operation. However, the longevity of this key part can vary widely depending on a number of factors.
The average lifespan of a car transmission varies between transmission types:
- Manual Transmissions: About 120,000 to 150,000 miles.
- Automatic Transmissions: Between 100,000 to 200,000 miles.
- Continuously Variable Transmissions (CVT): Approximately 100,000 miles.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the factors that affect the longevity of your car’s transmission, and highlight the telltale signs of transmission issues.
Fundamentals of Car Transmissions
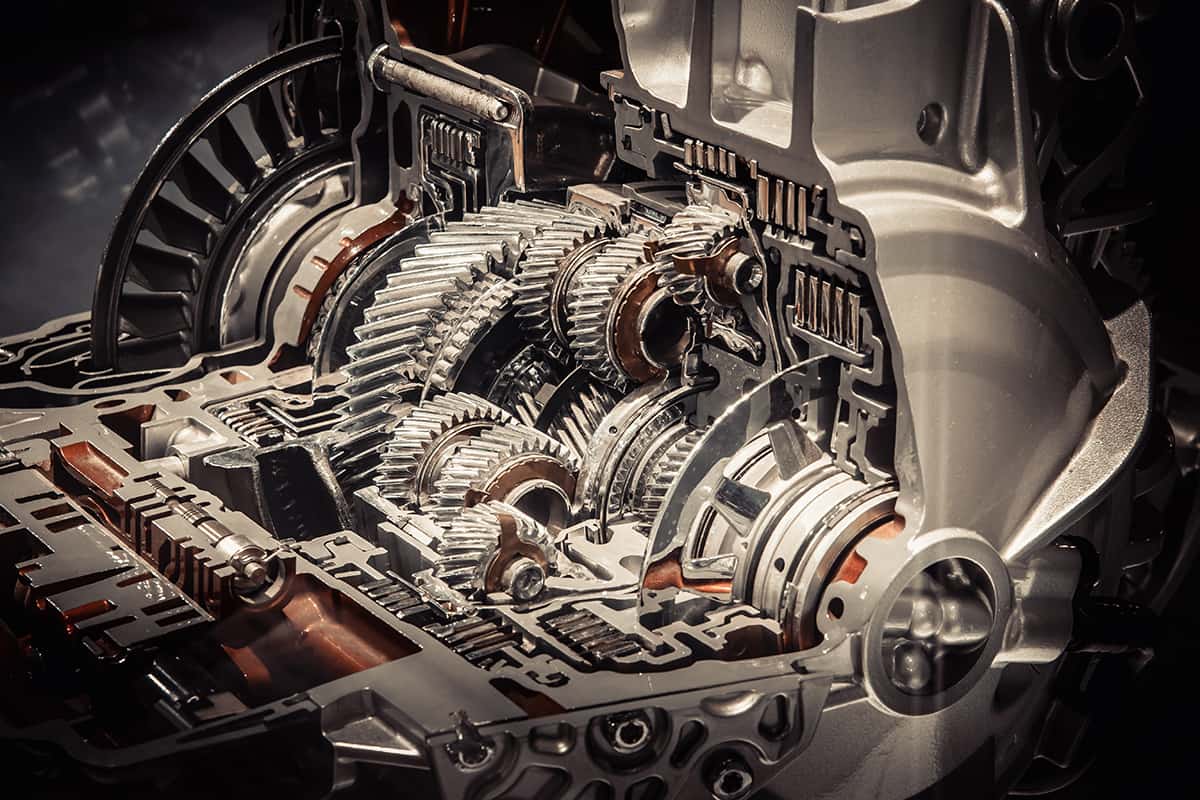
The transmission acts as the bridge between the engine and the wheels. It controls the power sent to the wheels, keeping the engine within an optimal range of RPMs while providing various speeds.
The primary parts of transmission include the clutch, gearbox, propeller shaft, differential, and axles. The clutch connects or disconnects the engine’s power to the gearbox. The gearbox allows for various speeds by modifying the power received from the clutch. The propeller shaft and differential transfer power from the gearbox to the axles, which then rotate the wheels.
Average Lifespan of a Car Transmission
The lifespan of your car’s transmission is subject to several factors, including the type of transmission your vehicle employs. This integral component’s longevity can range broadly, which is why understanding the average lifespan can be a great starting point.
1. Lifespan of Manual Transmissions
Manual transmissions, known for their resilience and simplicity, tend to have a longer lifespan. When well-maintained and used correctly, a manual transmission can easily last between 120,000 to 150,000 miles.
2. Lifespan of Automatic Transmissions
Automatic transmissions are a bit more complex in their operation, which makes them prone to potential issues. Generally, an automatic transmission can last between 100,000 to 200,000 miles.
3. Lifespan of Continuously Variable Transmissions (CVT)
Continuously Variable Transmissions (CVT) have become increasingly popular in modern vehicles for their fuel efficiency and seamless shifting. However, this comes at the cost of durability. A CVT typically lasts for just around 100,000 miles.
Factors Affecting Car Transmission Lifespan
The lifespan of your car’s transmission isn’t set in stone. Various factors come into play that can either prolong or shorten it.
Driving Habits and Their Impact on Transmission Longevity
The way you drive can significantly affect the lifespan of your transmission. Aggressive driving, such as rapid acceleration, hard braking, and high-speed driving, can put excessive stress on the transmission, leading to faster wear and tear.
Consistently riding the clutch in a manual transmission, or shifting from drive to reverse before a complete stop in an automatic transmission, can also damage the transmission over time.
Role of Regular Maintenance in Transmission Lifespan
Regular maintenance is a crucial factor in your transmission’s longevity. This includes regular checks and replacement of the transmission fluid, which helps to lubricate and cool the transmission’s internal components.
Influence of Terrain and Driving Conditions
The type of terrain you typically drive on and the overall driving conditions can also affect your transmission’s life. For instance, driving in hilly areas that require frequent shifting, or in heavy stop-and-go traffic, can increase wear on the transmission.
Similarly, driving in extreme temperatures, either very hot or very cold, can put additional strain on the transmission.
Effect of Towing Heavy Loads
Towing heavy loads puts extra strain on your transmission as it has to work harder to deliver the needed power. Consistently towing heavy loads without properly equipping your vehicle can cause your transmission to overheat and wear out faster.
Signs of Transmission Problems

Recognizing the early signs of transmission problems can save you from costly repairs or even complete transmission failure.
The following signs indicate that your transmission requires attention. If you experience any of these symptoms, you should have your vehicle inspected by a professional immediately. The earlier a transmission problem is identified and addressed, the better chance you have of preventing more serious damage.
Here are some common symptoms of transmission problems and what they could potentially mean.
1. Transmission Slipping
If your vehicle feels like it’s changing gears on its own or isn’t accelerating as it should, it’s possible your transmission is slipping. This could manifest as a loss of power while driving, or the engine might sound like it’s whining. These issues can indicate wear and tear in your transmission’s bands or gears.
2. Delayed Engagement
When there’s a delay between the moment you shift from “Park” to “Drive” and when the car actually starts moving, it’s known as delayed engagement. This is a common symptom of a transmission problem and should be addressed promptly.
3. Fluid Leaks
If you notice a leak or spots under your parked vehicle, it’s important to check your transmission fluid levels. The fluid should be bright red, clear, and have a slightly sweet smell when in good condition. A change in color or smell may indicate a problem.
4. Transmission Warning Light
Modern vehicles have a transmission warning light (often labeled as “Check Engine”) on the dashboard. If this light comes on, it’s a clear sign that something could be wrong with your transmission. You should get your vehicle inspected as soon as possible.
5. Odd Sounds
Unusual sounds like humming, clunking, or whining are often signs of transmission problems. These sounds might be more noticeable in certain gears or at specific speeds.
6. Burning Smell
A burning smell from your vehicle is never a good sign. It could mean your transmission is overheating, often due to low fluid levels or using the wrong type of transmission fluid.
7. Difficulty Shifting Gears
If your vehicle refuses to go into gear, it’s a clear sign of transmission trouble. This could be due to low fluid levels, the wrong type or viscosity of the fluid, or severe internal issues.
8. Grinding or Shaking
A functioning transmission should transition smoothly between gears. If your car jerks, grinds, or shakes during a gear change, this is a symptom of transmission trouble.






