An unwelcome sound from your car’s engine ranks among the worst imaginable disturbances. When the engine is normally quiet and reliable, any noises it makes are extremely annoying. If you’ve ever heard a knocking noise while the engine was idling, you might be curious about its source and what it could mean.
Knocking or tapping noises from the engine could mean that your car is running out of oil. This could indicate the need for maintenance on the engine or the replacement of a worn valve or lifter.
In this guide, we’ll go over the different engine noises and what could be the cause behind your car engine’s knocking sounds at idle.
Types of Irregular Engine Sounds
There are a few sounds you should listen to when turning your car’s engine on.
Whistling
Car whistling is a high-pitched sound that occurs when the engine coolant has reached its boiling temperature and excess pressure is escaping. This sound is an indication of an overheating engine and can indicate a serious problem that needs to be addressed by a mechanic.
When you hear this sound, it is important to be cautious and avoid touching the radiator cap as it can result in burns. Additionally, this issue is often accompanied by steam and an engine temperature warning light. If you hear this sound, it is recommended to stop driving the car and call a tow truck to have the matter looked at by a professional.
Screeching
Screeching noises in a vehicle are typically caused by the engine belts slipping on metal pulleys. This can happen when the rubber belt is not properly tensioned or has become old and worn, resulting in a glazed, cracked, or brittle surface. Improper tension, engine heat, dirt, and general wear can all cause damage to the belts.
It is important to maintain the correct belt tension because it ensures that the belts run smoothly along the pulleys and transfers the engine’s energy to power systems like the air conditioning, alternator, and water pump. If the tension is too low, the belts could come off completely, cause premature wear, and slip, resulting in the screeching noise.
Grinding
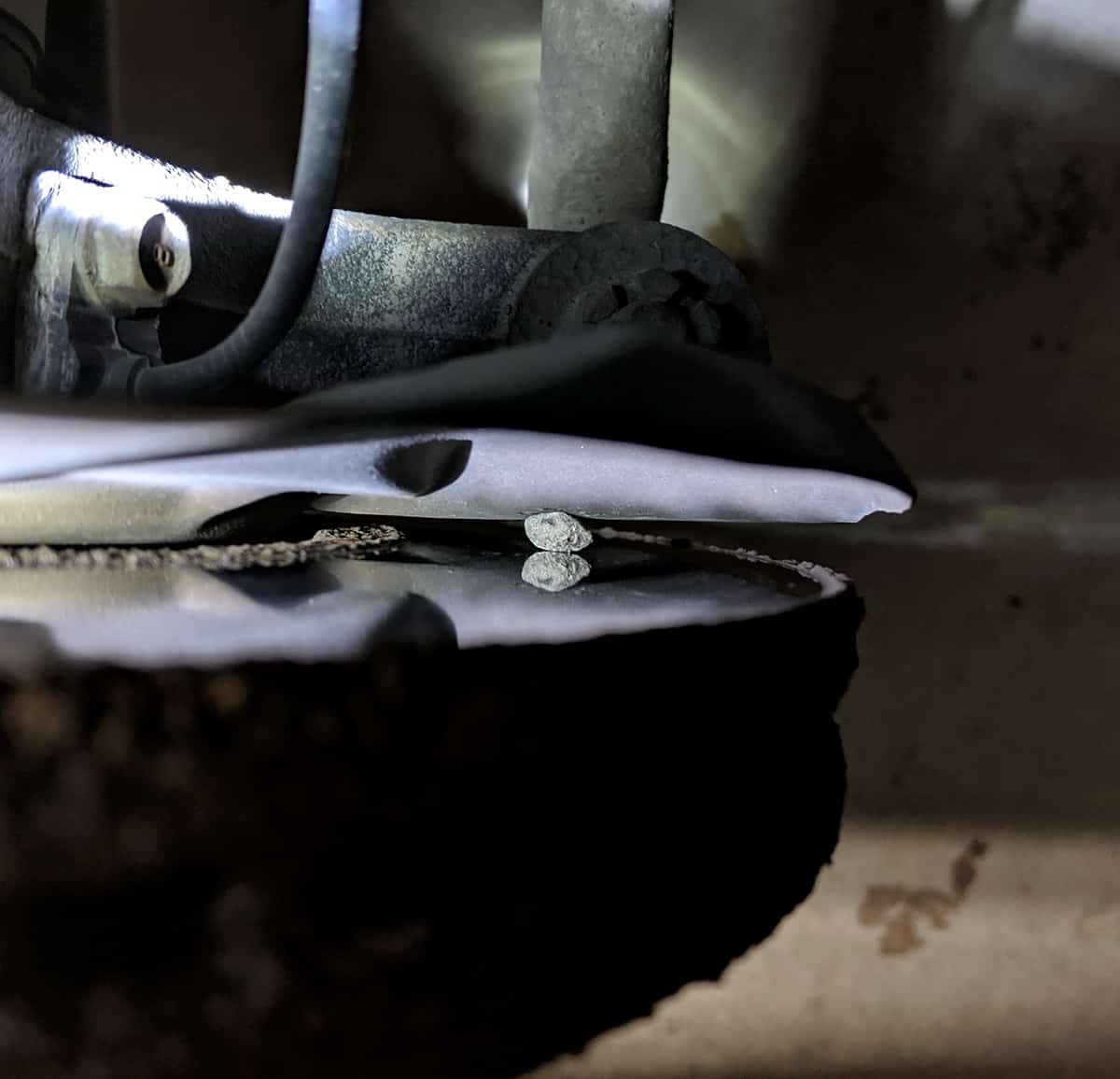

A grinding noise in a car is often an indication of a problem with the brakes. If you hear a metal-on-metal grinding noise coming from your car, it is likely that the brake pads have worn down completely and the metal brake rotor and caliper are now grinding against each other.
This type of brake issue can cause damage to the braking system, reduce braking performance, and be unsafe. If you hear a grinding noise coming from your brakes, it is important to have them inspected and repaired as soon as possible by a qualified mechanic. Delaying brake repairs can result in further damage, increased repair costs, and potentially dangerous driving conditions.
Knocking
Engine knocking or tapping is a common term used to describe a metallic knocking or ticking sound that originates from an engine. This type of noise is typically caused by the engine’s connecting rods not moving smoothly in their crankshaft bores or by abnormal combustion within the engine.
Engine knocking can be caused by a variety of factors such as poor fuel quality, incorrect ignition timing, low engine oil pressure, worn engine components, and more. This type of noise can cause serious damage to an engine if left unaddressed.
Engine Knocking at Idle—Causes and Fixes
Now, let’s take a close look at the most common causes of why your car’s engine makes annoying knocking sounds when idling.
1. Spark plugs
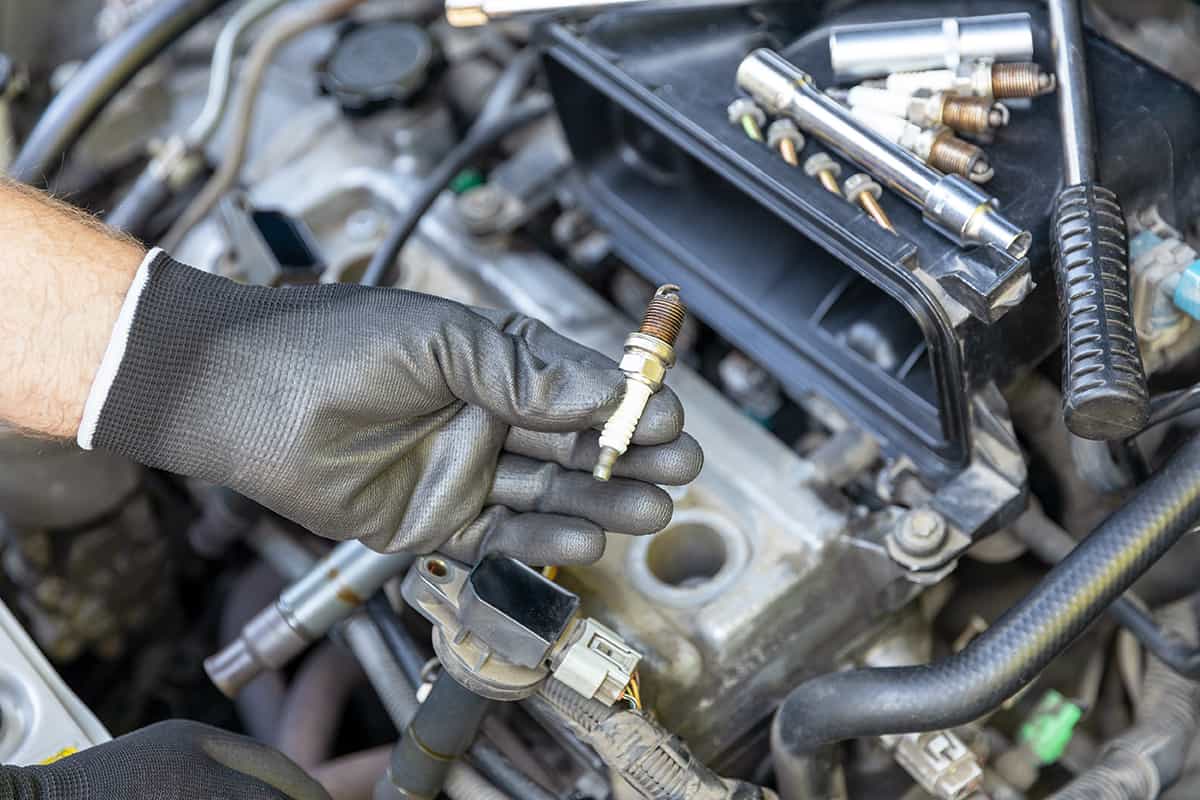

A spark plug is a component of a gasoline engine that ignites the fuel-air mixture in the cylinders with an electric spark. The spark plug is an essential component of an engine’s combustion process and contributes to its smooth and efficient operation.
If one or more of an engine’s spark plugs are worn or damaged, the engine may produce a knocking or tapping sound. This can occur if the spark plug is misfiring, resulting in an incomplete combustion of the fuel-air mixture. This may cause unburned fuel to be expelled from the engine, resulting in a knocking or tapping sound. The incorrect firing of the spark plug can also result in misfires, which can cause engine knocking.
2. Fuel choice
Gasoline, diesel, ethanol, and propane are the most common types of fuel used in motor vehicles. Each type of fuel has a unique set of properties and characteristics that determine its suitability for various engine types.
Inadequate fuel selection can result in knocking engine sounds in a variety of ways. If a vehicle designed to run on regular unleaded gasoline is fueled with diesel, engine knocking can occur because diesel fuel ignites differently than gasoline and can cause abnormal combustion in the engine. Using inferior-quality gasoline that contains impurities or contaminants can also result in engine knocking, as these impurities can interfere with the combustion process.
3. Knock sensor
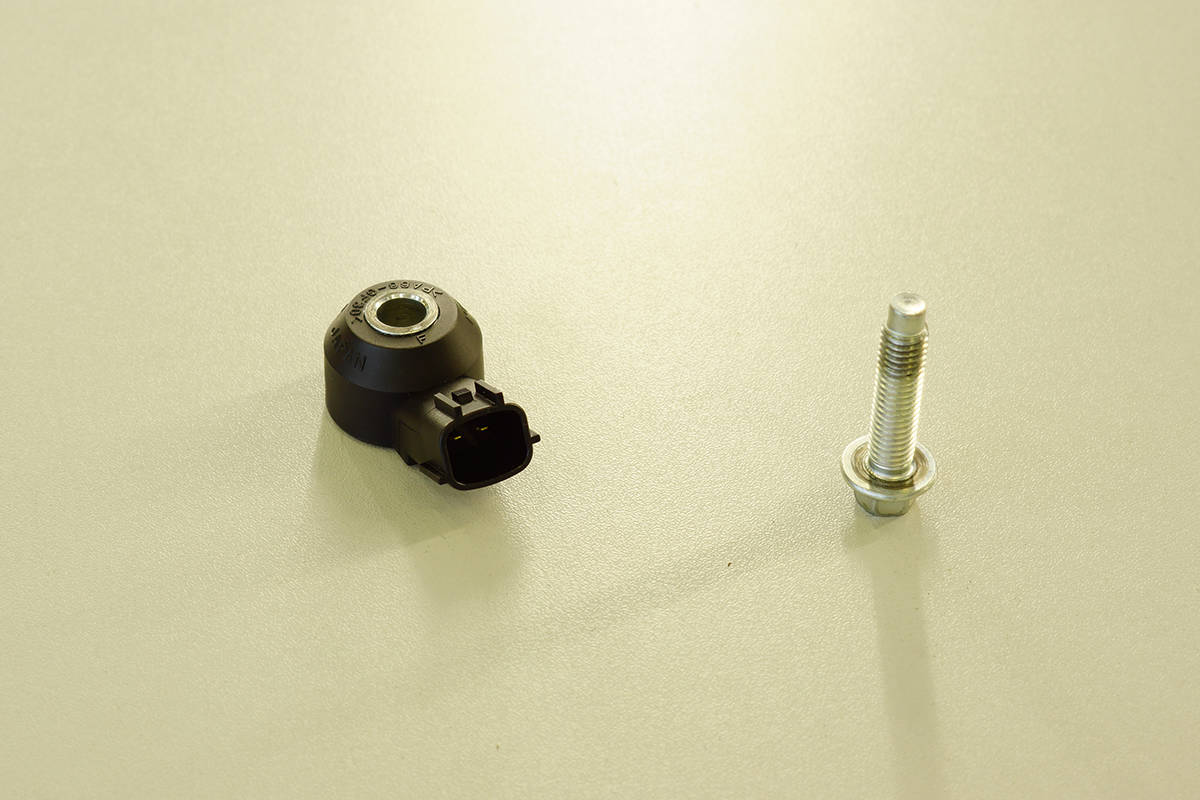

A knock sensor is a component of a modern engine management system that detects knocking or pinging sounds caused by abnormal combustion in the engine. The knock sensor transmits a signal to the engine control module, which adjusts the ignition timing to prevent further knocking and prevent engine damage.
It is essential to have your knock sensor inspected and, if necessary, replaced, as a faulty knock sensor can not only cause engine knocking but also affect the engine’s performance and fuel economy. Regular maintenance and inspection of the knock sensor is essential to maintaining a healthy engine and avoiding costly repairs in the future.
4. Air-fuel mixture
The air-fuel mixture is the mixture of air and fuel delivered to the engine’s cylinders for combustion and power production. Known as the stoichiometric ratio, the optimal air-fuel ratio is approximately 14.7 parts air to 1 part fuel.
A number of engine knocking sounds can be caused by an unbalanced air-fuel mixture. If the air-fuel mixture is too rich, meaning that there is an excess of fuel relative to air, it can result in pre-ignition, where the fuel ignites prematurely in the combustion chamber, resulting in abnormal combustion and knocking sounds. Alternatively, if the air-fuel ratio is too lean, meaning there is an excess of air relative to fuel, it can result in engine misfires and knocking sounds.
5. Bearings
Bearings are mechanical components that support and direct rotating engine components, including the crankshaft and connecting rods. They are designed to reduce friction and wear, facilitating the engine’s smooth operation.
In numerous ways, worn bearings can cause knocking engine sounds. As bearings deteriorate, they can become loose, resulting in excessive motion in the engine components they support. This may cause metal-on-metal contact between components, resulting in knocking noises. In addition, worn bearings can result in increased friction, which can increase noise and heat.
6. Bolts
Loose engine bolts can cause knocking noises by allowing engine components to shift and move, thereby increasing friction and vibration. This can cause metal-on-metal contact between components, resulting in knocking noises. Loss of engine performance and efficiency, as well as an increase in fuel consumption, can be caused by loose bolts.
Numerous factors, such as vibration, exposure to heat and moisture, or simple aging, can result in loose bolts. It is essential to inspect and tighten any loose engine bolts on a regular basis to ensure that all engine components are securely fastened and that the engine operates smoothly and efficiently.
7. Pistons
Pistons are cylindrical components that move up and down within the cylinders of an engine to produce the combustion that drives the engine. They are essential to the operation of the engine.
In multiple ways, defective pistons can cause knocking engine sounds. If the pistons are harmed or worn, they may not move freely within the cylinders, resulting in increased friction and vibration. This can cause metal-on-metal contact between components, resulting in knocking noises.
8. Valve guides
Valve guides are small cylindrical components that provide a smooth surface for the up-and-down movement of the engine’s valves. They are located in the cylinder head of the engine and are designed to allow the valves to move freely and precisely.
By permitting the valves to move irregularly, resulting in increased friction and vibration, worn valve guides can cause knocking engine sounds. This can cause metal-on-metal contact between components, resulting in knocking noises. In addition, worn valve guides can reduce engine performance and efficiency and increase fuel consumption.
Can You Resolve the Engine Knocking at Idle?
Yes, engine knocking at idle can be resolved, depending on the underlying cause. If the engine is irreparably damaged, the only way to guarantee that the knocking noise is eliminated is to replace the entire engine. If the problem is caused by a minor issue that can be resolved by replacing a few parts, a mechanic can perform the required repairs.
In either case, it is essential to have a qualified mechanic diagnose the issue and determine the most appropriate course of action. If necessary, replacing the engine with a used one can save money while ensuring that the knocking noise is eliminated.