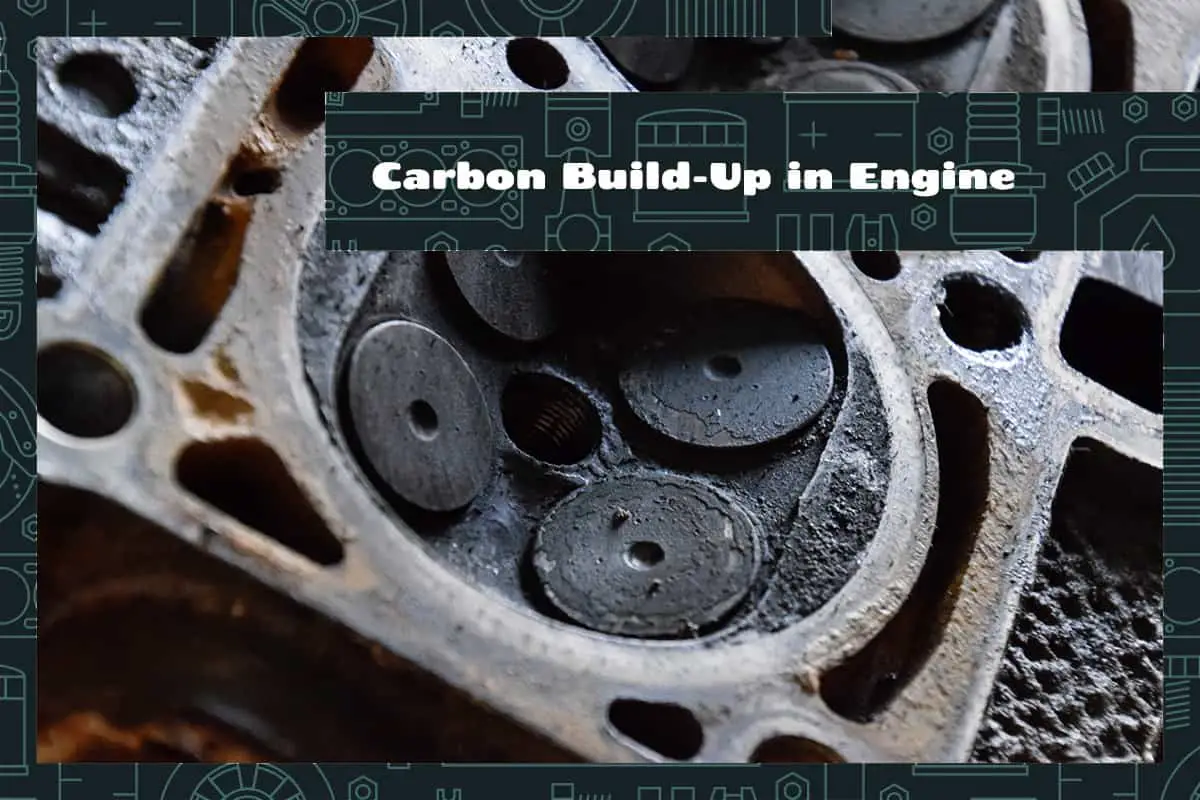
Carbon build-up in an engine is a widespread automotive issue that can hinder your vehicle’s performance over time. While this might seem like a technical concern only mechanics need to worry about, it has a real impact on your vehicle. A clear understanding of carbon build-up can help you better maintain your vehicle and address potential problems early.
Identifying carbon build-up in your engine can be tricky, as it manifests through several symptoms over time. This might include:
- Decreased fuel efficiency
- Reduced engine performance
- Engine misfires and vibrations
- Increased emissions
- Check engine light
In this short guide, we will dive deeper into the causes, and signs of carbon build-up, as well as explore the methods used to remove it.
A Closer Look at Carbon Build-up

In simplest terms, carbon build-up is a natural byproduct of combustion—the process that powers your vehicle. Your car’s engine works by burning a mix of air and fuel. This combustion releases energy to propel your vehicle, but it also results in exhaust gasses. While the majority of these gasses are expelled from the engine through the exhaust system, some unburnt fuel particles, or “carbon,” can stick to the internal parts of the engine.
These particles accumulate, forming layers of carbon deposits on key components such as the intake valves, fuel injectors, cylinder heads, and combustion chamber. This is what we call carbon build-up. It’s like the plaque that builds up in our arteries—it may seem inconsequential at first, but over time it can severely impact the engine’s functionality.
Why does carbon build-up occur? It boils down to the fact that not all the fuel-air mixture in your engine burns completely during combustion. Different factors can influence how efficiently your engine burns fuel, from the type of fuel and oil you use to your driving habits and even the design of the engine itself.
Causes of Carbon Build-up in Engines
By identifying the root causes, we can formulate strategies to prevent its occurrence and prolong engine lifespan. Let’s dive into the factors contributing to carbon accumulation in your engine.
1. Direct Injection
In the quest for better fuel economy and power, many car manufacturers have adopted Gasoline Direct Injection (GDI) technology. With GDI, fuel is sprayed directly into the combustion chamber rather than the intake tract. This design enhances fuel-air mixing, which boosts power and efficiency.
However, GDI engines can be more susceptible to carbon build-up. In older port injection engines, fuel is mixed with air before reaching the intake valves, effectively cleaning them with each cycle. But in GDI engines, fuel bypasses the intake valves entirely, leading to potential carbon build-up on these components.
2. Fuel Quality
Fuel can be found in various types of octanes. Low-quality fuels often have more contaminants that can create carbon residues. They may lack the detergent additives in higher-quality fuels designed to keep engines clean.
3. Engine Oil
Engine oil’s primary function is lubricating engine parts, but it also acts as a cleaning agent, helping to remove some carbon particles. If oil changes are neglected or if low-quality oil is used, carbon can accumulate more quickly. Old or degraded oil loses its ability to effectively lubricate and clean, and low-quality oils may not have the detergents needed to keep carbon in check.
4. Driving Habits
Your driving habits can play a significant role in carbon build-up. Short trips and city driving often don’t allow the engine to reach optimal temperatures for efficient combustion, leading to incomplete fuel burning and carbon deposits. Moreover, hard accelerations can also create conditions for more incomplete combustion, contributing to carbon build-up.
Symptoms to Look Out For
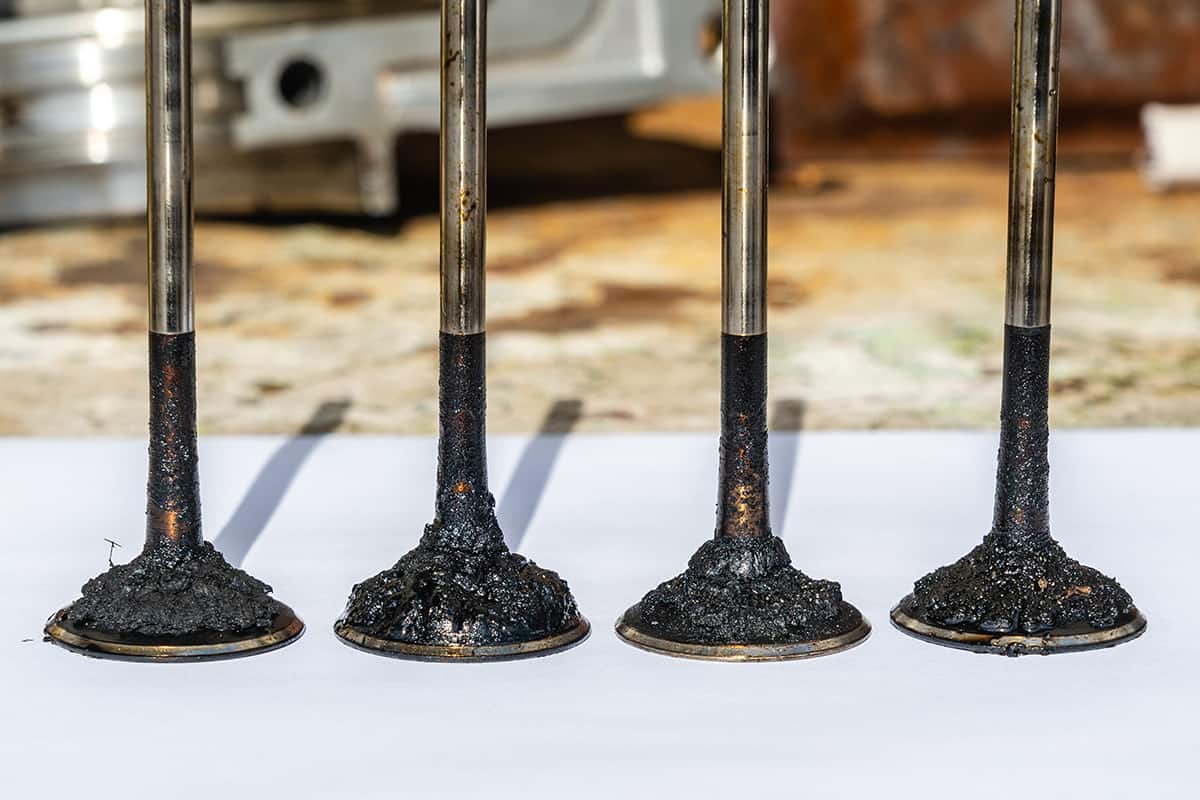

Carbon build-up can compromise the engine’s functionality, but recognizing the symptoms early can help you prevent potential engine damage. Here’s what to watch out for.
1. Decreased Fuel Efficiency
As carbon deposits restrict airflow or impair the operation of fuel injectors, your engine might consume more fuel to compensate for these deficiencies. If you notice your vehicle is not achieving the same miles per gallon as before, it might be due to carbon build-up.
2. Reduced Engine Performance
This could manifest as sluggish acceleration, a lack of power when driving uphill, or a general sense of your vehicle ‘struggling’ during operation. If you notice any decline in your car’s performance, it’s worth considering whether carbon build-up might be a contributing factor.
3. Engine Misfires and Vibrations
Misfires often happen because carbon deposits on the spark plugs can prevent them from creating the spark needed for combustion. Similarly, carbon on the intake valves can lead to them not closing properly, disrupting the engine’s operation. This can result in a rough idle, jerky acceleration, or even difficulty starting the car.
4. Increased Emissions
This happens because carbon deposits can disrupt the fuel-air mixture in the engine, leading to inefficient combustion and higher levels of pollutants. In some cases, this could cause your vehicle to fail an emissions test.
5. Check Engine Light
The check engine light can illuminate for a multitude of reasons, and carbon build-up is one of them. Excessive carbon deposits can cause your engine to run poorly, and the vehicle’s onboard computer might turn on the check engine light in response.
While this light is not a definitive indication of carbon build-up, carbon build-up could be the issue if it comes on in conjunction with any of the above symptoms.
Carbon Build-up Removal Methods
Recognizing carbon build-up is only half the battle; the other half involves effective removal. Luckily, there are several methods to cleanse your engine of carbon deposits, each with its benefits and drawbacks. Let’s explore these techniques.
1. Chemical Cleaners
Chemical cleaners often come in liquid form and are conveniently added to fuel or oil. They aim to circulate throughout the engine system, reaching the nooks and crannies where carbon deposits may have formed. As the engine operates, the heat from combustion or the mechanical action of lubrication can help these cleaners dissolve the stubborn carbon deposits that hinder engine performance.
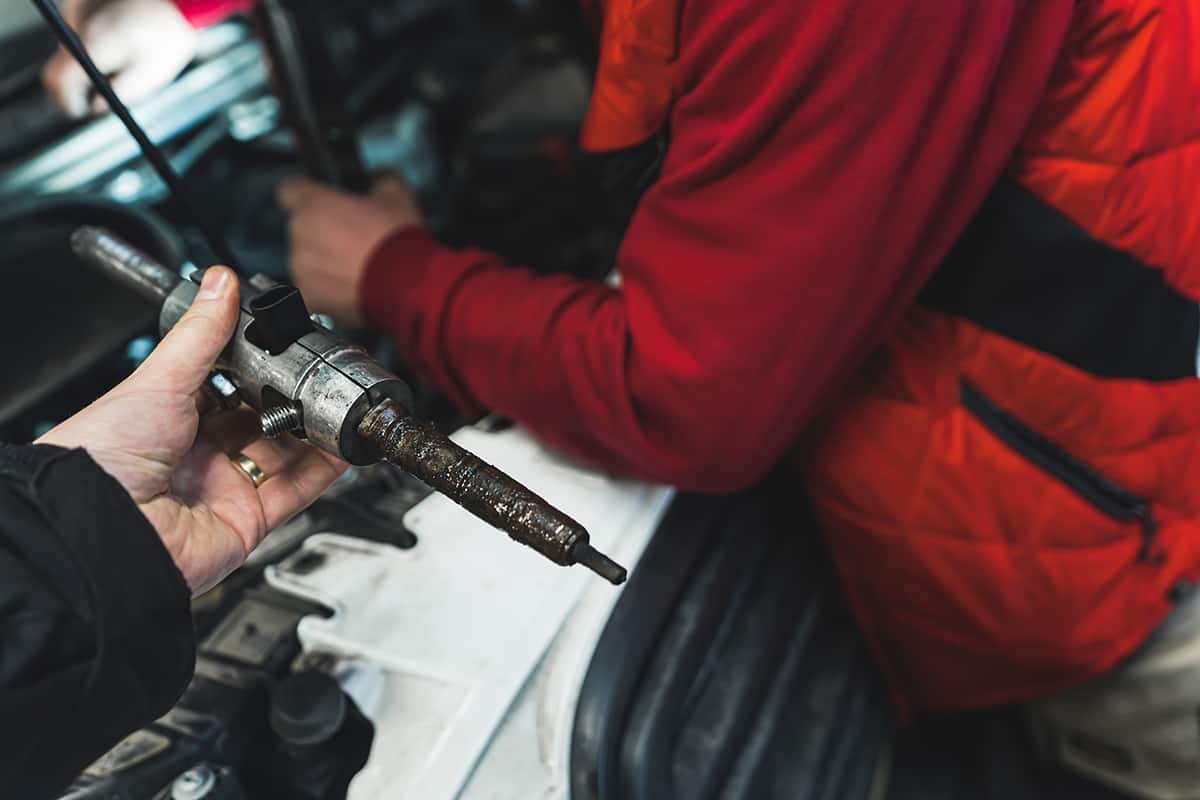
2. Fuel System Cleaning
Fuel system cleaning is a specialized procedure involving the use of potent chemicals to effectively cleanse the fuel injectors, intake valves, and combustion chambers of your engine. These chemicals act like powerful detergents, breaking down the carbon deposits that have formed in these critical engine components.
This method is particularly advantageous when dealing with severe carbon build-up, as the strong chemicals are often more effective than standard chemical cleaners in tackling stubborn carbon deposits.
3. Walnut Blasting
Walnut blasting is a more intensive cleaning method for severe carbon build-up. The process involves blasting crushed walnut shells into the intake tract while the engine is off, effectively ‘scrubbing’ off the carbon deposits. While walnut blasting can be extremely effective, it’s also invasive and should be performed by a professional to avoid any damage to the engine.
4. Catalytic Converter Cleaner
The catalytic converter, an essential component of the vehicle’s exhaust system, can also suffer from carbon build-up, leading to reduced efficiency and increased emissions.
Catalytic converter cleaners are products designed to clean this component. They are added to the fuel and work as the vehicle is driven. While not directly addressing carbon in the engine, keeping the catalytic converter clean can help the overall function of the engine and reduce emissions.
5. Regular Engine Maintenance
While not a removal method per se, regular engine maintenance is key to preventing carbon build-up in the first place. This includes regular oil changes, high-quality fuel, and ensuring your engine runs correctly. Preventative maintenance is often the most cost-effective method of dealing with carbon build-up.