Cars have evolved dramatically over the decades, introducing an array of technologies to protect drivers and passengers during an accident. At the heart of this evolution is the Service Safety Restraint System, a sophisticated combination of seat belts, airbags, and sensors designed to reduce injury during a crash.
Faults in the Service Safety Restraint System can arise from mechanical wear and tear, accidents, or electrical issues. Addressing these promptly ensures the system functions correctly. Solutions range from regular maintenance checks to seeking professional repairs.
This guide will explore the components of the safety restraint system, common issues they face, and actionable solutions to keep them in optimal condition.
Components of the Safety Restraint System
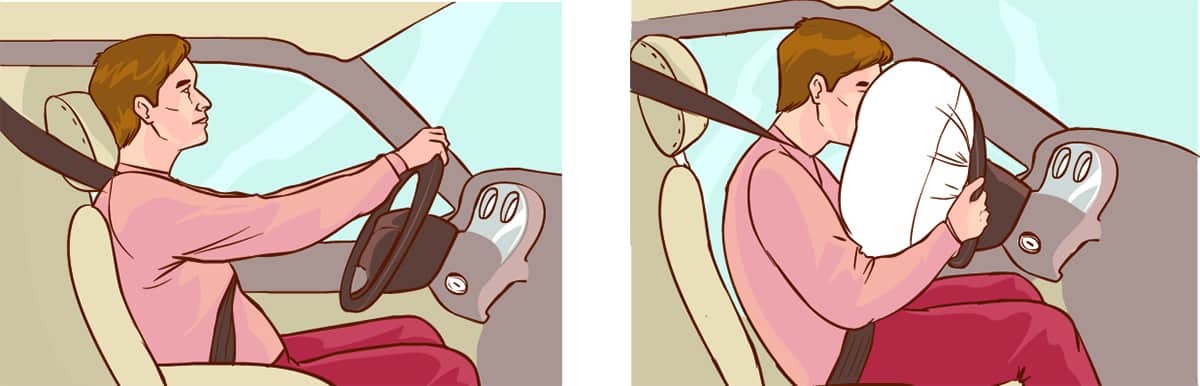
The Service Safety Restraint System, often simply referred to as the safety restraint system, is an integrated ensemble of devices in your car, engineered to safeguard passengers during unexpected events or accidents. This system encompasses a variety of components that work together seamlessly.
1. Seat Belts
Seat belts are the most recognizable component of the restraint system. They’re designed to keep passengers securely in place, minimizing movement during sudden stops or impacts.
The primary role of the seat belt is to distribute the force of a sudden stop or impact over larger parts of the body, like the pelvis and chest, which can handle more stress. By doing so, they prevent passengers from being thrown forward or from side to side, minimizing potential injuries.
2. Airbags
Airbags serve as a supplementary protective measure to seat belts, offering an added layer of safety. When a severe impact occurs, airbags inflate in milliseconds, cushioning passengers from hard surfaces inside the car.
Airbags use sensors that detect sudden deceleration, signaling the bags to inflate. They fill up with nitrogen gas, forming a soft cushion between passengers and the interior of the vehicle. After the initial impact, the airbags start to deflate to help absorb some of the force, further reducing the chance of injury.
Common Causes of Restraint System Failures
While modern cars come equipped with advanced safety measures, failures can still occur due to various reasons.
1. Mechanical Wear and Tear
Every part of a vehicle undergoes wear, and the safety restraint system is no exception.
- Aging components and materials: Continuous use of seat belts can lead to fraying or weakening, especially near the anchor points or within the retractor mechanism. Likewise, the materials inside airbags, like the propellant that inflates them, can degrade over time, affecting their deployment speed and efficiency.
- Repeated use and stress points: Buckling and unbuckling seat belts or subjecting them to sudden jerks can put stress on specific points, leading to potential breakages. For instance, the seatbelt latch can wear out, affecting its locking capability.
2. Accidents and Physical Damage
Any collision, whether major or minor, can impact the effectiveness of the restraint system components.
- Impact-related malfunctions: Even if airbags deploy correctly during an accident, they’re designed for a single use. This means that after an accident, they need replacing. Moreover, the force of a collision can damage seat belts, especially if they absorbed a significant portion of the impact, rendering them less effective for future use.
- Post-accident inspections: Following a collision, it’s not always evident that a part of the safety restraint system is damaged. Internal components, like sensors or the airbag’s inflation mechanism, may suffer unseen damages. Therefore, post-accident checks by professionals are advised to ensure everything is in working order.
3. Electrical Issues
With the integration of technology, many components of the restraint system rely on electrical functions.
- Wiring and connection faults: The restraint system’s effectiveness hinges on a network of wires and connections. These connections can become loose, corroded, or broken with time. This can prevent signals from reaching airbags or seatbelt tensioners, hindering their function. For instance, a corroded wire might delay an airbag’s deployment.
- Sensor malfunctions: Airbags deploy based on signals from sensors that detect collisions. If these sensors malfunction due to dirt accumulation, water damage, or other issues, they might send incorrect signals. This could lead to airbags deploying unexpectedly or not deploying when needed.
Fixes and Solutions for Restraint System Issues

Addressing the aforementioned issues can be straightforward if you know what to look for and how to tackle them.
1. Addressing Mechanical Wear and Tear
Dealing with the natural aging of vehicle components is inevitable, but with regular maintenance and vigilance, the safety of the restraint system can be upheld.
- Regularly inspect seat belts for signs of fraying, tearing, or excessive slack. If you find any of these signs, it’s time to replace the belt. Some vehicles come with seatbelt tensioners that can be adjusted to ensure the belt fits snugly, enhancing its protective ability.
- Airbags contain materials that can degrade. While they have a long lifespan, if you own an older vehicle, consider having an automotive professional inspect the airbag system to ensure it’s still functional.
2. Post-Accident Repairs
After a collision, even if the damage seems minimal, it’s essential to assess the Service Safety Restraint System to ensure future safety.
- If your airbags deployed during an accident, they need to be replaced immediately. Airbags are designed for single-use, and once they’ve been activated, they can’t be reused.
- After an accident, the force exerted on seat belts might compromise their integrity. While they might look fine, their internal structure could be weakened. Have them inspected by a professional, and if in doubt, replace them.
3. Resolving Electrical Issues
It is essential to keep the wiring and sensors of the safety restraint system in top condition.
- Sensors that detect collisions and deploy airbags can accumulate dirt or suffer from water damage. Regularly cleaning and ensuring they’re free from obstructions can maintain their effectiveness. If they show signs of malfunctioning, like an airbag warning light on your dashboard, they may need replacement.
- The myriad of wires and connectors ensuring the safety restraint system works seamlessly can become loose or corroded. Regularly checking them, especially after any work has been done on your car, can prevent unexpected issues. If you’re experiencing problems, a comprehensive electrical system check by an automotive technician can pinpoint and rectify the problem.
4. Periodic Maintenance and Professional Checks
The best way to guarantee the functionality of any system is through regular maintenance and professional oversight.
- Just as you would check the oil or brakes, include a restraint system check in your regular car maintenance routine. This way, you can spot potential issues before they escalate.
- While many fixes can be DIY, the intricacies of the Service Safety Restraint System can sometimes require a professional touch. If you’re ever unsure about any component, consult a mechanic or technician who specializes in automotive safety systems.
FAQs
1. How often should I get my restraint system checked?
You should inspect your restraint system annually as part of your regular vehicle maintenance. However, if you notice any issues like frayed seat belts or if your car has been involved in a collision, you should get it checked immediately regardless of the last inspection.
2. What does it mean when the airbag light stays on?
If the airbag light remains illuminated, it typically indicates a potential issue with your car’s airbag system. This could be due to a variety of reasons, such as a malfunctioning sensor, electrical faults, or problems with the airbag itself. Get it checked out ASAP.
3. How long do airbags last in a vehicle?
Airbags are designed to last the lifetime of most vehicles, typically around 10-15 years. However, factors like environmental conditions and the car’s overall wear can influence their lifespan.