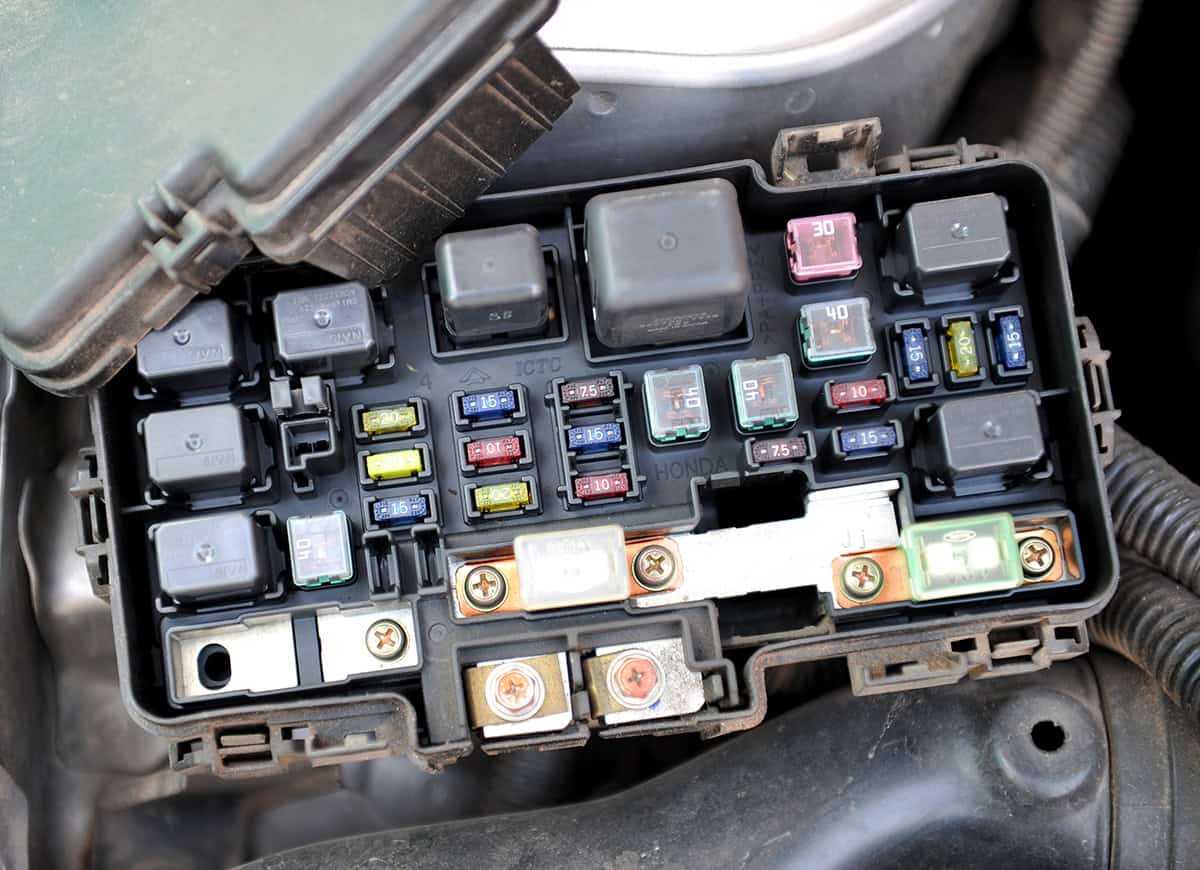
Our vehicles rely on a number of important components to function properly, and the alternator fuse is one of them. The fuse is a crucial safeguard that prevents damage to the alternator and other electrical components. Just like any other part of a vehicle, the alternator fuse can fail, leading to a variety of issues.
The main causes and fixes for a blown alternator fuse include:
- Overcharging of the alternator
- Electrical shorts
- Faulty wiring or connections
- Overloading the electrical system
- Age and wear
The simplest solution to a blown alternator fuse is to replace it with a fresh one.
In this article, we will explore the various causes of a blown alternator fuse and provide a step-by-step guide on how to replace the bad fuse.
Intro to Alternator Fuses
The alternator is an important part of a car because it charges the battery and powers the electrical system when the engine is running. The alternator fuse is like a safety device that protects the alternator and other electrical parts from damage.
Function of the alternator
The alternator makes electricity when the engine is running and sends it to the battery, so the battery stays charged. It also provides power to the lights, radio, and other electrical devices in the car.
Role of the alternator fuse
The alternator fuse is a small but important part that protects the alternator and the rest of the electrical system. If there’s too much electricity, the fuse will break or “blow” to stop the flow of power. This prevents damage to the alternator and other parts of the car.
Types of alternator fuses
There are different types of alternator fuses, but they all do the same job; namely, protect the electrical system. Some common types are blade fuses, which look like small, flat, colorful plugs, and cartridge fuses, which are small, cylindrical, and made of plastic or glass.
Identifying a Blown Alternator Fuse
Figuring out if your alternator fuse is blown can help you solve problems with your car’s electrical system. Here are some ways to identify a blown fuse:
Symptoms of a blown fuse
If your alternator fuse is blown, you might notice some of the following signs:
- Dead battery
- Electrical issues
- Engine stalling
- Warning lights
- Burning smell
Testing the alternator fuse
To test the fuse, you can use a tool called a multimeter and follow these steps:
- Obtain a multimeter and set it to the lowest resistance setting.
- Locate the fuse you want to test and remove it from the circuit.
- Hold the fuse up to a light source or inspect it visually to check for any visible signs of damage or a broken wire inside the fuse.
- Touch one probe of the multimeter to each end of the fuse.
- If the multimeter shows a number close to zero, the fuse is good and does not need to be replaced.
- If the multimeter shows a high number or doesn’t change, the fuse is probably blown and needs to be replaced.
Common Causes of a Blown Alternator Fuse
There are several reasons why an alternator fuse might blow. Let’s look at some common causes:
1. Overcharging of the alternator
Sometimes, the alternator can produce too much electricity, causing the fuse to blow. This is called overcharging. It can happen if the voltage regulator, a part that controls the amount of electricity the alternator makes, is not working properly.
2. Electrical shorts
An electrical short is when electricity takes a shortcut and flows along an unintended path. This can cause too much electricity to flow through the fuse, making it blow. Electrical shorts can happen due to damaged wires, worn-out insulation, or loose connections.
3. Faulty wiring or connections
Damaged, worn-out, or loose wires or connections in your car’s electrical system can cause the fuse to blow. It’s important to check and repair any faulty wiring to prevent further damage to the electrical system.
4. Overloading the electrical system
Adding too many electrical accessories to your car, like powerful audio systems, lights, or chargers, can overload the electrical system. If the system has to handle more power than it was designed for, the fuse might blow to protect the alternator and other components.
5. Age and wear
Over time, fuses can become weak and break or blow even under normal conditions. This is because the metal inside the fuse can wear out from the constant flow of electricity. Older fuses are more likely to blow because they may not be able to handle the same amount of power as a new fuse.
Step-by-Step Guide to Fixing a Blown Alternator Fuse
If you’ve determined that your alternator fuse is blown, you can follow these steps to fix it:
Step 1. Disconnecting the battery
Before you start, make sure the car is off and the keys are out of the ignition. Open the hood and disconnect the battery by removing the negative cable first, then the positive cable. This is a safety precaution to avoid getting shocked or damaging the electrical system.
Step 2. Locating and removing the blown fuse
Find the fuse box under the hood of your car. It may have a label or diagram showing which fuse is for the alternator. If you’re not sure, check your car’s manual or look online for information about your specific make and model. Once you’ve found the alternator fuse, use a fuse puller or a pair of needle-nose pliers to carefully remove it.
Step 3. Inspecting and testing the alternator
Before replacing the fuse, inspect the alternator for signs of damage, like burnt wires or a cracked casing. If the alternator looks okay, you can test it using a multimeter. Set the multimeter to the voltage setting, and with the engine running, touch the probes to the battery terminals. The multimeter should read around 13.7 to 14.7 volts. If it reads lower or higher, the alternator may be faulty and need replacement.
Step 4. Installing the new fuse
Get a new fuse with the same rating as the blown one. Place the new fuse in the correct slot in the fuse box. Make sure it’s firmly seated and secure.
Step 5. Reconnecting the battery and testing the system
Reconnect the battery by attaching the positive cable first, then the negative cable. Start the car and check the electrical system to make sure everything is working properly. If the fuse blows again or the electrical system is still not working, there may be a more serious issue that requires professional help.
FAQs
1. How do I know if my alternator fuse is blown?
If your alternator fuse is blown, you might notice symptoms like the car not starting, the battery dying quickly, or the lights and other electrical devices not working properly. To confirm, you can test the fuse using a multimeter.
Set it to the lowest resistance setting and touch the probes to each end of the fuse. If the reading is close to zero, the fuse is good. If it shows a high number or doesn’t change, the fuse is likely blown.
2. How long does it take to replace an alternator fuse?
Replacing an alternator fuse is usually a quick process and can take about 15 to 30 minutes. However, the time it takes may vary depending on the location of the fuse box, the type of fuse used, and your experience with cars.
3. What happens if I use the wrong fuse rating for my alternator?
Using the wrong fuse rating for your alternator can cause problems with your car’s electrical system.
If the fuse rating is too low, it may blow even under normal conditions, leading to frequent fuse replacements and potential damage to the alternator. If the fuse rating is too high, it may not blow when it should, allowing too much electricity to flow and potentially damaging the alternator and other electrical components.